Page 188 - Materials Science and Engineering An Introduction
P. 188
160 • Chapter 5 / Diffusion
List of Symbols
Symbol Meaning
A Cross-sectional area perpendicular to direction of diffusion
C Concentration of diffusing species
Initial concentration of diffusing species prior to the onset of the
C 0
diffusion process
C s Surface concentration of diffusing species
C x Concentration at position x after diffusion time t
D Diffusion coefficient
D 0 Temperature-independent constant
M Mass of material diffusing
Q d Activation energy for diffusion
#
R Gas constant (8.31 J/mol K)
t Elapsed diffusion time
Position coordinate (or distance) measured in the direction of diffusion,
x
normally from a solid surface
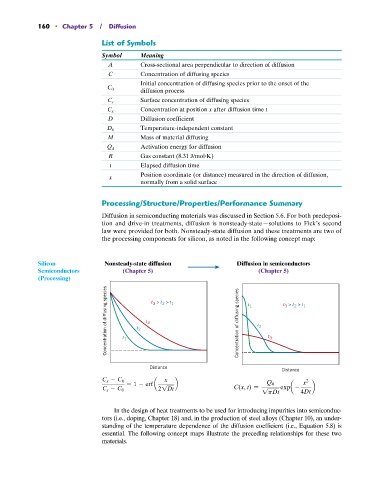
Processing/Structure/Properties/Performance Summary
Diffusion in semiconducting materials was discussed in Section 5.6. For both predeposi-
tion and drive-in treatments, diffusion is nonsteady-state—solutions to Fick’s second
law were provided for both. Nonsteady-state diffusion and these treatments are two of
the processing components for silicon, as noted in the following concept map:
Silicon Nonsteady-state diffusion Diffusion in semiconductors
Semiconductors (Chapter 5) (Chapter 5)
(Processing)
Concentration of diffusing species t 1 t 2 t 3 t > t > t Concentration of diffusing species t 1 t 2 t 3 t > t > t
3 2 1
3 2 1
Distance
Distance
x 2
C x - C 0
= 1 - erf a b Q 0 x
C s - C 0 21Dt C(x, t) = expa - b
1pDt 4Dt
In the design of heat treatments to be used for introducing impurities into semiconduc-
tors (i.e., doping, Chapter 18) and, in the production of steel alloys (Chapter 10), an under-
standing of the temperature dependence of the diffusion coefficient (i.e., Equation 5.8) is
essential. The following concept maps illustrate the preceding relationships for these two
materials.