Page 93 - Materials Science and Engineering An Introduction
P. 93
3.8 Point Coordinates • 65
EXAMPLE PROBLEM 3.5
Location of Point Having Specified Coordinates
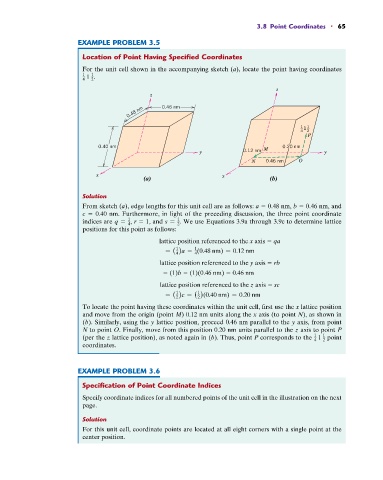
For the unit cell shown in the accompanying sketch (a), locate the point having coordinates
1 1
2
4 1 .
z
z
0.48 nm 0.46 nm
1 1 1
4 2
P
0.40 nm M 0.20 nm
y 0.12 nm y
N 0.46 nm O
x x
(a) (b)
Solution
From sketch (a), edge lengths for this unit cell are as follows: a 0.48 nm, b 0.46 nm, and
c 0.40 nm. Furthermore, in light of the preceding discussion, the three point coordinate
1
1
indices are q = , r 1, and s = . We use Equations 3.9a through 3.9c to determine lattice
2
4
positions for this point as follows:
lattice position referenced to the x axis qa
= ( )a = (0.48 nm) = 0.12 nm
1
1
4 4
lattice position referenced to the y axis rb
(1)b (1)(0.46 nm) 0.46 nm
lattice position referenced to the z axis sc
1
1
= ( )c = ( )(0.40 nm) = 0.20 nm
2 2
To locate the point having these coordinates within the unit cell, first use the x lattice position
and move from the origin (point M) 0.12 nm units along the x axis (to point N), as shown in
(b). Similarly, using the y lattice position, proceed 0.46 nm parallel to the y axis, from point
N to point O. Finally, move from this position 0.20 nm units parallel to the z axis to point P
(per the z lattice position), as noted again in (b). Thus, point P corresponds to the 1 point
1
1
2
4
coordinates.
EXAMPLE PROBLEM 3.6
Specification of Point Coordinate Indices
Specify coordinate indices for all numbered points of the unit cell in the illustration on the next
page.
Solution
For this unit cell, coordinate points are located at all eight corners with a single point at the
center position.