Page 105 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 105
92 2 Solid-State Chemistry
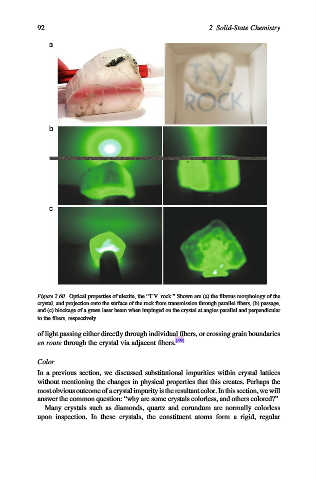
Figure 2.60. Optical properties of ulexite, the “T.V. rock.” Shown are (a) the fibrous morphology of the
crystal, and projection onto the surface of the rock from transmission through parallel fibers, (b) passage,
and (c) blockage of a green laser beam when impinged on the crystal at angles parallel and perpendicular
to the fibers, respectively.
of light passing either directly through individual fibers, or crossing grain boundaries
en route through the crystal via adjacent fibers. [49]
Color
In a previous section, we discussed substitutional impurities within crystal lattices
without mentioning the changes in physical properties that this creates. Perhaps the
most obvious outcome of a crystal impurity is the resultant color. In this section,we will
answer the common question: “why are some crystals colorless, and others colored?”
Many crystals such as diamonds, quartz and corundum are normally colorless
upon inspection. In these crystals, the constituent atoms form a rigid, regular