Page 50 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 50
37
2.3. The Crystalline State
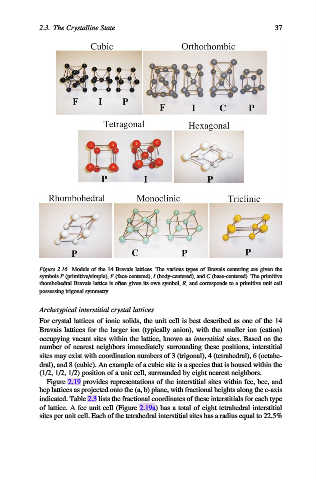
Figure 2.16. Models of the 14 Bravais lattices. The various types of Bravais centering are given the
symbols P (primitive/simple), F (face-centered), I (body-centered), and C (base-centered). The primitive
rhombohedral Bravais lattice is often given its own symbol, R, and corresponds to a primitive unit cell
possessing trigonal symmetry.
Archetypical interstitial crystal lattices
For crystal lattices of ionic solids, the unit cell is best described as one of the 14
Bravais lattices for the larger ion (typically anion), with the smaller ion (cation)
occupying vacant sites within the lattice, known as interstitial sites. Based on the
number of nearest neighbors immediately surrounding these positions, interstitial
sites may exist with coordination numbers of 3 (trigonal), 4 (tetrahedral), 6 (octahe-
dral), and 8 (cubic). An example of a cubic site is a species that is housed within the
(1/2, 1/2, 1/2) position of a unit cell, surrounded by eight nearest neighbors.
Figure 2.19 provides representations of the interstitial sites within fcc, bcc, and
hcp lattices as projected onto the (a, b) plane, with fractional heights along the c-axis
indicated. Table 2.3 lists the fractional coordinates of these interstitials for each type
of lattice. A fcc unit cell (Figure 2.19a) has a total of eight tetrahedral interstitial
sites per unit cell. Each of the tetrahedral interstitial sites has a radius equal to 22.5%