Page 61 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 61
48 2 Solid-State Chemistry
The equilibrium distribution of cations in tetrahedral and octahedral sites within
the spinel lattice depends on the size of the ionic radii, electrostatic energies, and
polarization effects. As one would expect, the degree of cation disorder will signifi-
cantly influence the magnetic properties of magnetic ferrite spinels. [21] One may
intentionally prepare spinels containing nonequilibrium cation distributions through
rapid quenching of sintered powders. For instance, when ground mixtures of MnO
and Al 2 O 3 powders are sintered and quenched the resulting (Mn x Al 1 x ) 3 O 4 spinel
has an oxygen-deficient metal:oxygen ratio of 3:3.7. [22] Another mixed ternary
system, Mn 1.5 0.5x Co 1þ0.5x Ni 0.5 O 4 (0 x 1.0), is used in negative temperature
coefficient (NTC) thermistors [23] for applications in a variety of electrical products,
communication and industrial equipment, and automobiles.
The Boltzmann distribution (Eq. 8) relates the dependence of temperature on the
amount of cation disorder in spinels, where E i is the activation energy required to
exchange interstitial sites of M 2þ and M 3þ cations (i.e., between tetrahedral and
octahedral sites, respectively). Energy values for these interchanges generally fall in
the range 0.11–0.14 eV.
ið1 þ iÞ E i
ð8Þ ¼ e kT ;
2
ð1 iÞ
where: i ¼ degree of inversion; normal spinel ¼ 0 and inverse spinel ¼ 1.
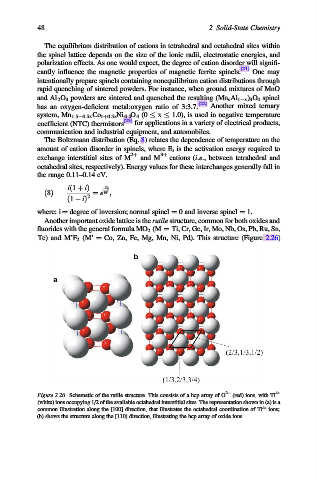
Another important oxide lattice is the rutile structure, common for both oxides and
fluorides with the general formula MO 2 (M ¼ Ti, Cr, Ge, Ir, Mo, Nb, Os, Pb, Ru, Sn,
Te) and M’F 2 (M’ ¼ Co, Zn, Fe, Mg, Mn, Ni, Pd). This structure (Figure 2.26)
Figure 2.26. Schematic of the rutile structure. This consists of a hcp array of O 2 (red) ions, with Ti 4+
(white) ions occupying 1/2 of the available octahedral interstitial sites. The representation shown in (a) is a
common illustration along the [100] direction, that illustrates the octahedral coordination of Ti 4+ ions;
(b) shows the structure along the [110] direction, illustrating the hcp array of oxide ions.