Page 60 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 60
47
2.3. The Crystalline State
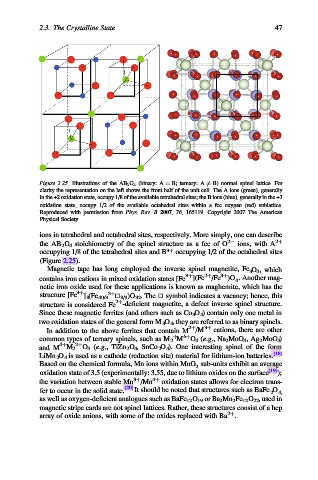
Figure 2.25. Illustrations of the AB 2 O 4 (binary: A ¼ B; ternary: A 6¼ B) normal spinel lattice. For
clarity the representation on the left shows the front half of the unit cell. The A ions (green), generally
in the +2 oxidation state, occupy 1/8 of the available tetrahedral sites; the B ions (blue), generally in the +3
oxidation state, occupy 1/2 of the available octahedral sites within a fcc oxygen (red) sublattice.
Reproduced with permission from Phys. Rev. B 2007, 76, 165119. Copyright 2007 The American
Physical Society.
ions in tetrahedral and octahedral sites, respectively. More simply, one can describe
the AB 2 O 4 stoichiometry of the spinel structure as a fcc of O 2 ions, with A 2þ
occupying 1/8 of the tetrahedral sites and B 3þ occupying 1/2 of the octahedral sites
(Figure 2.25).
Magnetic tape has long employed the inverse spinel magnetite, Fe 3 O 4 , which
2þ
3þ
3þ
contains iron cations in mixed oxidation states [Fe ](Fe /Fe )O 4 . Another mag-
netic iron oxide used for these applications is known as maghemite, which has the
3þ
3þ
structure [Fe ] 8 (Fe 40/3 □ 8/3 )O 32 . The □ symbol indicates a vacancy; hence, this
structure is considered Fe -deficient magnetite, a defect inverse spinel structure.
2þ
Since these magnetic ferrites (and others such as Co 3 O 4 ) contain only one metal in
two oxidation states of the general form M 3 O 4 , they are referred to as binary spinels.
2þ
In addition to the above ferrites that contain M /M 3þ cations, there are other
þ
6þ
common types of ternary spinels, such as M 2 M O 4 (e.g.,Na 2 MoO 4 ,Ag 2 MoO 4 )
4þ
2þ
and M M 2 O 4 (e.g., TiZn 2 O 4 , SnCo 2 O 4 ). One interesting spinel of the form
LiMn 2 O 4 is used as a cathode (reduction site) material for lithium-ion batteries. [18]
Based on the chemical formula, Mn ions within MnO 2 sub-units exhibit an average
oxidation state of 3.5 (experimentally: 3.55, due to lithium oxides on the surface [19] );
3þ
the variation between stable Mn /Mn 4þ oxidation states allows for electron trans-
fer to occur in the solid state. [20] It should be noted that structures such as BaFe 2 O 4,
as well as oxygen-deficient analogues such as BaFe 12 O 19 or Ba 2 Mn 2 Fe 12 O 22 , used in
magnetic stripe cards are not spinel lattices. Rather, these structures consist of a hcp
2þ
array of oxide anions, with some of the oxides replaced with Ba .