Page 145 - Mathematical Models and Algorithms for Power System Optimization
P. 145
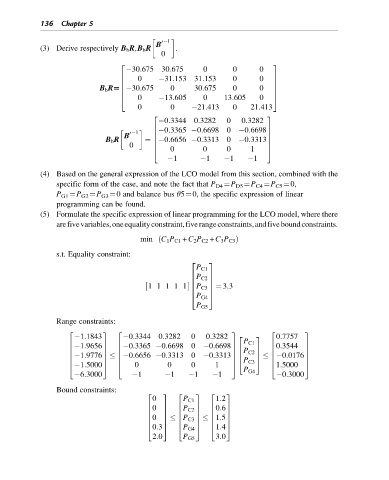
136 Chapter 5
B 0 1
(3) Derive respectively B b R,B b R .
0
2 3
30:675 30:675 0 0 0
6 0 31:153 31:153 0 0 7
6 7
B b R5 30:675 0 30:675 0 0 7
6
6 7
4 0 13:605 0 13:605 0 5
0 0 21:413 0 21:413
2 3
0:3344 0:3282 0 0:3282
0:3365 0:6698 0 0:6698
0 1 6 7
B 6 7
B b R ¼ 0:6656 0:3313 0 0:3313 7
6
0 6 7
0 0 0 1
4 5
1 1 1 1
(4) Based on the general expression of the LCO model from this section, combined with the
specific form of the case, and note the fact that P D4 ¼P D5 ¼P C4 ¼P C5 ¼0,
P G1 ¼P G2 ¼P G3 ¼0 and balance bus θ5¼0, the specific expression of linear
programming can be found.
(5) Formulate the specific expression of linear programming for the LCO model, where there
arefivevariables,oneequalityconstraint,fiverangeconstraints,andfiveboundconstraints.
min ð C 1 P C1 + C 2 P C2 + C 3 P C3 Þ
s.t. Equality constraint:
2 3
P C1
P C2
6 7
6 7
½ 11 11 1 P C3 7 ¼ 3:3
6
6 7
P G4
4 5
P G5
Range constraints:
2 3 2 3 2 3
1:1843 0:3344 0:3282 0 0:3282 2 3 0:7757
P C1
1:9656 0:3365 0:6698 0 0:6698 0:3544
6 7 6 7 6 7
6 7 6 76 P C2 7 6 7
1:9776 0:6656 0:3313 0 0:3313 0:0176
6 7 6 76 7 6 7
6 7 6 74 P C3 5 6 7
1:5000 0 0 0 1 1:5000
4 5 4 5 4 5
P G4
6:3000 1 1 1 1 0:3000
Bound constraints:
2 3 2 3 2 3
0 P C1 1:2
0 0:6
6 7 6 P C2 7 6 7
6 7 6 7 6 7
0 1:5
6 7 P C3 7 6 7
6
6 7 6 7 6 7
0:3 1:4
4 5 4 P G4 5 4 5
2:0 P G5 3:0