Page 309 - Mathematical Techniques of Fractional Order Systems
P. 309
298 Mathematical Techniques of Fractional Order Systems
(A) 5
Proposed REAL (U)
Compared REAL (U)
0
–5
–10
U (1)
–15
–20
–25
–30
0 10 20 30 40 50
Time (s)
(B) 20
Proposed REAL (U)
Compared REAL (U)
0
–20
–40
U (2)
–60
–80
–100
–120
0 10 20 30 40 50
Time (s)
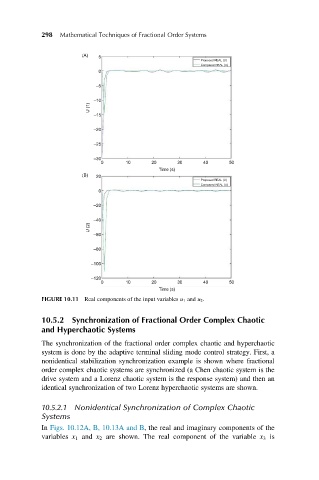
FIGURE 10.11 Real components of the input variables u 1 and u 2 .
10.5.2 Synchronization of Fractional Order Complex Chaotic
and Hyperchaotic Systems
The synchronization of the fractional order complex chaotic and hyperchaotic
system is done by the adaptive terminal sliding mode control strategy. First, a
nonidentical stabilization synchronization example is shown where fractional
order complex chaotic systems are synchronized (a Chen chaotic system is the
drive system and a Lorenz chaotic system is the response system) and then an
identical synchronization of two Lorenz hyperchaotic systems are shown.
10.5.2.1 Nonidentical Synchronization of Complex Chaotic
Systems
In Figs. 10.12A, B, 10.13A and B, the real and imaginary components of the
variables x 1 and x 2 are shown. The real component of the variable x 3 is