Page 210 - Mechanical design of microresonators _ modeling and applications
P. 210
0-07-145538-8_CH04_209_08/30/05
Microbridges: Lumped-Parameter Modeling and Design
Microbridges: Lumped-Parameter Modeling and Design 209
and (4.138) as the square root of the stiffness-to-inertia ratio, namely,
3
2
5.48(2+ c ) c t Gk t/ ȡ(c +2c ) l
t / 1
t 1
l
l
Ȧ t,e =
2
2
{ 32 + 10c (5+ 2c ) (t + w ) + c (30 + c (60 (4.139)
l
l
l
l
1
2
2 2
+c (40 + c (10 + c )))) c (c t + w )}/ (2+ c ) 4
l
l
t 1
l
l
t
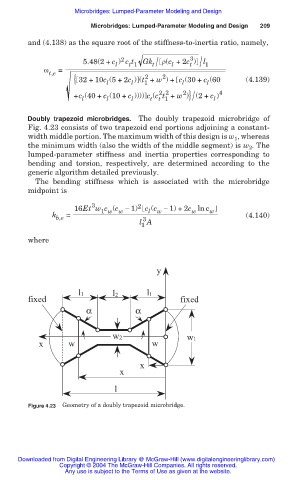
Doubly trapezoid microbridges. The doubly trapezoid microbridge of
Fig. 4.23 consists of two trapezoid end portions adjoining a constant-
width middle portion. The maximum width of this design is w , whereas
1
the minimum width (also the width of the middle segment) is w 2 . The
lumped-parameter stiffness and inertia properties corresponding to
bending and torsion, respectively, are determined according to the
generic algorithm detailed previously.
The bending stiffness which is associated with the microbridge
midpoint is
3
16Et w c (c í 1) 2 c (c í 1) +2c ln c w
l
w
w
w
1 w
k = (4.140)
b,e 3
l A
1
where
y
l1 l2 l1
fixed fixed
α α
w2 w1
x w w
x
x
l
Figure 4.23 Geometry of a doubly trapezoid microbridge.
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.