Page 132 - Mechanical Engineer's Data Handbook
P. 132
THERMODYNAMICS AND HEAT TRANSFER 121
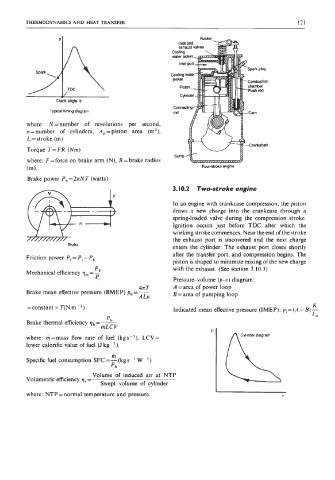
I
Coding
water jacket-.
Cooling water-
jackel Combustion
zmiw-I - Push md
chamber
Piston-
Cylinder -
Crank angle, e
Typical timing diagram
where: N =number of revolutions per second,
n =number of cylinders, A, =piston area (m'),
L = stroke (m)
Torque T=FR (Nm)
Sump
where: F=force on brake arm (N), R= brake radius
(m). Four-stmke engine
Brake power Pb=2nNT (watts)
3.10.2 Two-stroke engine
In an engine with crankcase compression, the piston
draws a new charge into the crankcase through a
spring-loaded valve during the compression stroke.
Ignition occurs just before TDC after which the
working stroke commences. Near the end of the stroke
7f/m7n3r Brake the exhaust port is uncovered and the next charge
enters the cylinder. The exhaust port closes shortly
after the transfer port, and compression begins. The
Friction power P, = Pi - P,
piston is shaped to minimize mixing of the new charge
with the exhaust. (See section 3.10.3)
'
b
Mechanical efficiency )I,,, = -
Pi Pressure-volume (pu) diagram:
4n T A =area of power loop
Brake mean effective pressure (BMEP) pb=- B = area of pumping loop
ALn
=constant x T(N m ~ *) K
Indicated mean effective pressure (IMEP): pi = (A - B) -
L*
'b
Brake thermal efficiency 9 -~
,-mLCV
where: m=mass flow rate of fuel (kgs-I), LCV=
lower calorific value of fuel (J kg-').
m
Specific fuel consumption SFC =- (kg s- ' W- ')
Pb
Volume of induced air at NTP
Volumetric efficiency )I,, =
Swept volume of cylinder
where: NTP = normal temperature and pressure. V