Page 84 - Mechanical Engineer's Data Handbook
P. 84
APPLIED MECHANICS 13
2.4.4 Cams
A cam is a mechanism which involves sliding contact
and which converts one type of motion into another,
e.g. rotary to reciprocating. Most cams are of the
radial type, but axial rotary cams are also used. Cams
may have linear motion. The motion is transmitted
through a ‘follower’ and four types are shown for
radial cams.
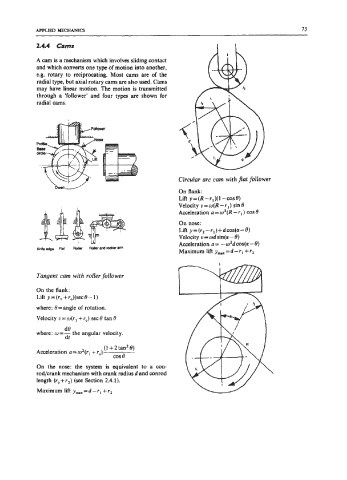
Circular arc cam with pat follower
On flank:
Lift y = (R -rl)( 1 -cos e)
Velocity o=o(R-r,) sin0
Acceleration a=w2(R-rl) cos0
On nose:
Lift y = (r2 - + d cos(a - e)
r
Velocity u = od sin@ - 0)
Acceleration a = - w2d cos(a - 0)
Maximum lift y,,=d-r, +r,
Tangent cam with roller follower
On the flank:
Lift y- (rl + rJ(sec0- 1)
where: 0=angle of rotation.
Velocity v=w(rl +ro) sec0 tan0
d0
where: w=- the angular velocity.
dt
(1 + 2 tanZ e)
Acceleration a = w2(rl + r,) cos e
On the nose: the system is equivalent to a con-
rodlcrank mechanism with crank radius d and conrod
length (ro+r2) (see Section 2.4.1).
Maximum lift y,,, = d - rl + r2