Page 808 - Mechanical Engineers' Handbook (Volume 2)
P. 808
3 Feedback Linearization Design of NN Tracking Controllers 799
keep the control u(t) finite. It is called a controller singularity problem if u(t) becomes
infinity. More advanced control is possible using novel techniques. One good example is the
use of integral Lyapunov functions in Refs. 20 and 21.
3.4 Partitioned NNs and Input Preprocessing
In this section we show how NN controller implementation may be streamlined by parti-
tioning the NN into several smaller subnets to obtain more efficient computation. Also dis-
cussed in this section is preprocessing of input signals for the NN to improve the efficiency
and accuracy of the approximation.
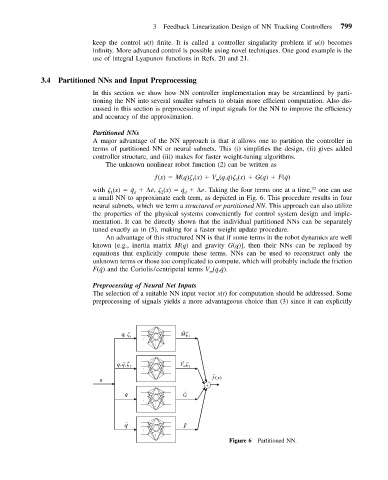
Partitioned NNs
A major advantage of the NN approach is that it allows one to partition the controller in
terms of partitioned NN or neural subnets. This (i) simplifies the design, (ii) gives added
controller structure, and (iii) makes for faster weight-tuning algorithms.
The unknown nonlinear robot function (2) can be written as
ƒ(x) M(q) (x) V (q,˙q) (x) G(q) F(˙q)
1
m
2
22
with (x) ¨q ˙e , (x) ˙q e . Taking the four terms one at a time, one can use
1 d 2 d
a small NN to approximate each term, as depicted in Fig. 6. This procedure results in four
neural subnets, which we term a structured or partitioned NN. This approach can also utilize
the properties of the physical systems conveniently for control system design and imple-
mentation. It can be directly shown that the individual partitioned NNs can be separately
tuned exactly as in (5), making for a faster weight update procedure.
An advantage of this structured NN is that if some terms in the robot dynamics are well
known [e.g., inertia matrix M(q) and gravity G(q)], then their NNs can be replaced by
equations that explicitly compute these terms. NNs can be used to reconstruct only the
unknown terms or those too complicated to compute, which will probably include the friction
F(˙q) and the Coriolis/centripetal terms V (q,˙q) .
m
Preprocessing of Neural Net Inputs
The selection of a suitable NN input vector x(t) for computation should be addressed. Some
preprocessing of signals yields a more advantageous choice than (3) since it can explicitly
q, ζ 1 ˆ M ˆ M 1 ζ 1 ζ
q, ζ 1
ζ
•
q, q ,q, ,ζ ˆ V ˆ V 2 ζ 2 ζ
2 2 m m
ˆ ˆ
(x)
f f (x )
x
+ +
q q G G ˆ ˆ
q • F ˆ F ˆ
Figure 6 Partitioned NN.