Page 216 - Mechanics Analysis Composite Materials
P. 216
Chapter 4. Mechanics of a composite layer 20 1
4.5.3. Free-edge efects
As shown in the previous section, there is a significant difference between
predicted and measured strength of an angle-ply specimen loaded in tension. This
difference is associated with the stress concentration that takes place in the vicinity
of the specimen longitudinal edges and was not taken into account in the analysis.
To study a free-edge effect in an angle-ply specimen, consider a strip whose initial
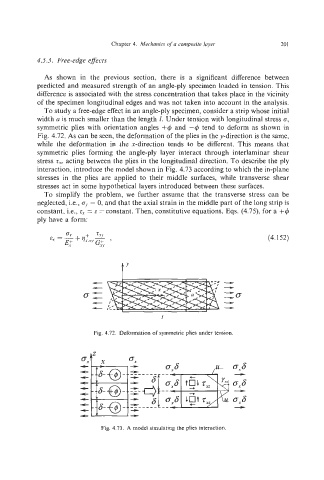
width a is much smaller than the length 1. Under tension with longitudinal stress c,
symmetric plies with orientation angles +4 and -4 tend to deform as shown in
Fig. 4.72. As can be seen, the deformation of the plies in the y-direction is the same,
while the deformation in the x-direction tends to be different. This means that
symmetric plies forming the angle-ply layer interact through interlaminar shear
stress z,; acting between the plies in the longitudinal direction. To describe the ply
interaction, introduce the model shown in Fig. 4.73 according to which the in-plane
stresses in the plies are applied to their middle surfaces, while transverse shear
stresses act in some hypothetical layers introduced between these surfaces.
To simplify the problem, we further assume that the transverse stress can be
neglected, i.e., a,: = 0, and that the axial strain in the middle part of the long strip is
constant, Le., cX = E =constant. Then, constitutive equations, Eqs. (4.75), for a +4
ply have a form:
(4.152)
t'
I
Fig. 4.72. Deformation of symmetric plies under tension.
Fig. 4.73. A model simulating the plies interaction.