Page 355 - Mechanics Analysis Composite Materials
P. 355
340 Mechanics and analysis of Composite materials
I
-
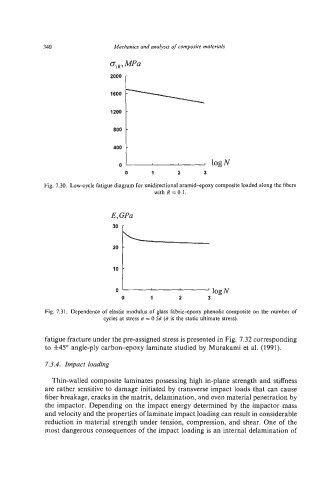
1200
-
800
-
400 -logN
0
0 1 2 3
Fig. 7.30. Low-cycle fatigue diagram for unidirectional aramid-epoxy composite loaded along the fibers
with R =0.1.
E,GPa
30 r
2o10 i
0 0I----- 1 2 3 logN
Fig. 7.31. Dependence of elastic modulus of glass fabric-epoxy phenolic composite on the number of
cycles at stress D = 0.55 (if is the static ultimate stress).
fatigue fracture under the pre-assigned stress is presented in Fig. 7.32 corresponding
to f45"angle-ply carbon-epoxy laminate studied by Murakami et al. (1 991).
7.3.4. Impact loading
Thin-walled composite laminates possessing high in-plane strength and stiffness
are rather sensitive to damage initiated by transverse impact loads that can cause
fiber breakage, cracks in the matrix, delamination, and even material penetration by
the impactor. Depending on the impact energy determined by the impactor mass
and velocity and the properties of laminate impact loading can result in considerable
reduction in material strength under tension, compression, and shear. One of the
most dangerous consequences of the impact loading is an internal delamination of