Page 357 - Mechanics Analysis Composite Materials
P. 357
342 Mechanics and analysis of composite niateriab
q.-Iso-
l
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
0 -Ei,Jlmm
0 5 10 15 20
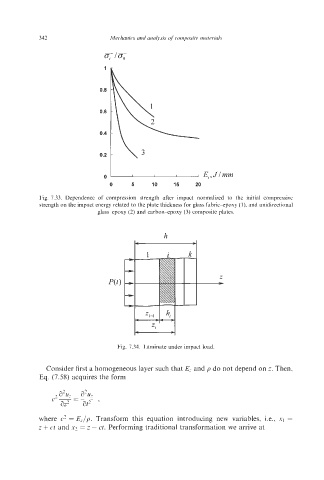
Fig. 7.33. Dependence of compression strength after impact normalized to the initial compressive
strength on the impact energy related to the plate thickness for glass fabric-epoxy (I), and unidirectional
glass-epoxy (2) and carbon-epoxy (3) composite plates.
h
I- -1
Fig. 7.34. Laminate under impact load.
Consider first a homogeneous layer such that E, and p do not depend on z. Then,
Eq. (7.58) acquires the form
where c2 = E,/p. Transform this equation introducing new variables, Le., XI =
z + ct and x2 = z - ct. Performing traditional transformation we arrive at