Page 181 - Mechanics of Microelectromechanical Systems
P. 181
168 Chapter 3
The terms in the right-hand side of Eq. (3.111) are the axial stiffnesses of the
two compliant members, taken with respect to their local frames (their x-axes
are parallel to their length dimensions).
The spring stiffness about the out-of-the-plane motion (the z-direction)
of the mass can be found by also using Fig. 3.37. A force is applied at
point 1 about the z-direction and the corresponding (out-of-the-plane)
displacement can be determined by considering bending and torsion of the
two compliant members. The z-direction stiffness of the half-model is:
which is valid when the two compliant segments are of constant cross-
sections. The whole folded-beam microspring is formed of two parallel-
connection identical parts (as the one sketched in Fig. 3.37), and therefore the
stiffness of the full microspring is:
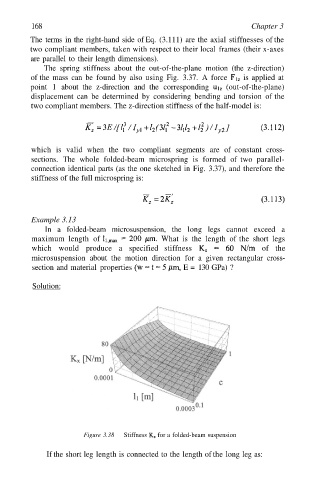
Example 3.13
In a folded-beam microsuspension, the long legs cannot exceed a
maximum length of What is the length of the short legs
which would produce a specified stiffness of the
microsuspension about the motion direction for a given rectangular cross-
section and material properties E = 130 GPa) ?
Solution:
Figure 3.38 Stiffness for a folded-beam suspension
If the short leg length is connected to the length of the long leg as: