Page 287 - Mechanics of Microelectromechanical Systems
P. 287
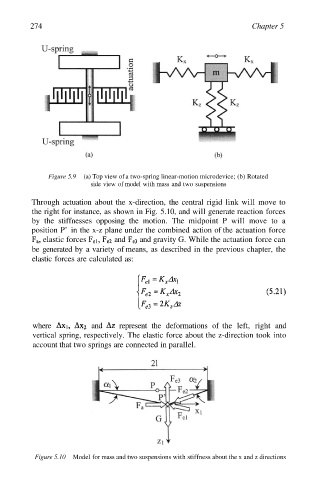
274 Chapter 5
Figure 5.9 (a) Top view of a two-spring linear-motion microdevice; (b) Rotated
side view of model with mass and two suspensions
Through actuation about the x-direction, the central rigid link will move to
the right for instance, as shown in Fig. 5.10, and will generate reaction forces
by the stiffnesses opposing the motion. The midpoint P will move to a
position P’ in the x-z plane under the combined action of the actuation force
elastic forces and and gravity G. While the actuation force can
be generated by a variety of means, as described in the previous chapter, the
elastic forces are calculated as:
where and represent the deformations of the left, right and
vertical spring, respectively. The elastic force about the z-direction took into
account that two springs are connected in parallel.
Figure 5.10 Model for mass and two suspensions with stiffness about the x and z directions