Page 332 - Mechanics of Microelectromechanical Systems
P. 332
5. Static response of MEMS 319
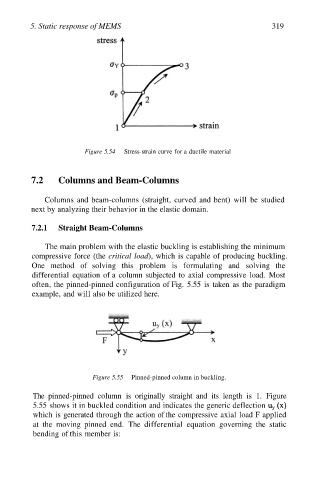
Figure 5.54 Stress-strain curve for a ductile material
7.2 Columns and Beam-Columns
Columns and beam-columns (straight, curved and bent) will be studied
next by analyzing their behavior in the elastic domain.
7.2.1 Straight Beam-Columns
The main problem with the elastic buckling is establishing the minimum
compressive force (the critical load), which is capable of producing buckling.
One method of solving this problem is formulating and solving the
differential equation of a column subjected to axial compressive load. Most
often, the pinned-pinned configuration of Fig. 5.55 is taken as the paradigm
example, and will also be utilized here.
Figure 5.55 Pinned-pinned column in buckling.
The pinned-pinned column is originally straight and its length is 1. Figure
5.55 shows it in buckled condition and indicates the generic deflection
which is generated through the action of the compressive axial load F applied
at the moving pinned end. The differential equation governing the static
bending of this member is: