Page 160 - Mechanism and Theory in Organic Chemistry
P. 160
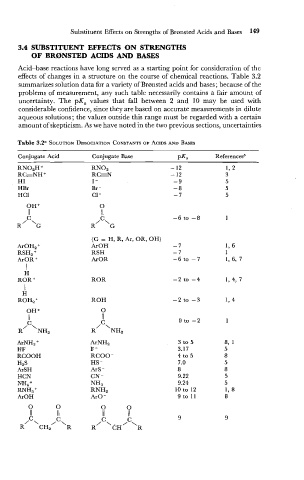
Substituent Effects on Strengths of Bronsted Acids and Bases 149
3.4 SUBSTITUENT EFFECTS ON STRENGTHS
OF BR0NSTED ACIDS AND BASES
Acid-base reactions have long served as a starting point for consideration of the
effects of changes in a structure on the course of chemical reactions. Table 3.2
summarizes solution data for a variety of Brcansted acids and bases; because of the
problems of measurement, any such table necessarily contains a fair amount of
uncertainty. The pK, values that fall between 2 and 10 may be used with
considerable confidence, since they are based on accurate measurements in dilute
aqueous solutions; the values outside this range must be regarded with a certain
amount of skepticism. As we have noted in the two previous sections, uncertainties
Table 3.2a SOLUTION DISSOCIATION CONSTANTS ACIDS AND BASES
OF
Conjugate Acid Conjugate Base PK, Referencesb
RN02 - 12 1, 2
RN02H +
RCENH + RGN - 12 3
HI I - -9 5
HBr Br- -8 5
HCl C1- -7 5
(G = H, R, Ar, OR, OH)
ArOH -7
ArOH2 +
RSH - 7
RSH2 +
ArOR -6 to -7
ArOR +
I
H
ROR -2 to -4
ROR +
ROH
ROH, +
ArNH,
ArNH3 +
HF F -
RCOOH RCOO-
H2S HS -
ArSH ArS -
HCN CN -
NH3
NH4 +
RNH2
RNH3 +
ArOH ArO-
0 0