Page 161 - Mechanism and Theory in Organic Chemistry
P. 161
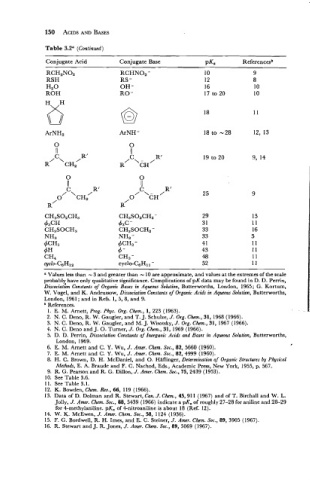
Table 3.2a (Continued)
Conjugate Acid Conjugate Base PKG Referencesb
RCH2N02 RCHN02 -
RSH RS -
Hz0 OH -
ROH RO-
ArNH -
CH3S02CH2-
43c -
CH3SOCH2 -
NH2-
4CH2 -
4 -
CH, -
cycle-CeHl, -
a Values less than N 3 and greater than - 10 are approximate, and values at the extremes of the scale
probably have only qualitative significance. Complications of pK data may be found in D. D. Perrin,
~issociat!on Constants of Organic Bases in Aquous Solution, Butterworths, London, 1965; G. Kortum,
W. Vogel, and K. Andrussow, Dissociation Constants of Organic Acids in Aqueous Solution, Butterworths,
London, 1961 ; and in Refs. 1,5,8, and 9.
References.
1. E. M. Arnett, Prog. Phys. Org. Chem., 1, 223 (1963).
2. N. C. Deno, R. W. Gaugler, and T. J. Schulze, J. Org. Chem., 31, 1968 (1966).
3. N. C. Deno, R. W. Gaugler, and M. J. Wisotsky, J. Org. Chem., 31, 1967 (1966).
4. N. C. Deno and J. 0. Turner, J. Org. Chem., 31, 1969 (1966).
5. D. D. Perrin, Dissociation Constants of Inorganic Acids and Bases in Aqueous Solution, Butterworths,
London, 1969.
6. E. M. Arnett and C. Y. Wu, J. Amer. Chem. Soc., 82, 5660 (1960).
7. E. M. Arnett and C. Y. Wu, J. Amer. Chem. Soc., 82, 4999 (1960).
8. H. C. Brown, D. H. McDaniel, and 0. Haflinger, Determination of Organic Structures by Physical
Methods, E. A. Braude and F. C. Nachod, Eds., Academic Press, New York, 1955, p. 567.
9. R. G. Pearson'and R. G. Dillon, J. Amr. Chem. Soc., 75, 2439 (1953).
10. See Table 3.6.
11. See Table 3.1.
12. K. Bowden, Chem. Rev., 66, 119 (1966).
13. Data of D. Dolman and R. Stewart, Can. J. Chern., 45,911 (1967) and of T. Birchall and W. L.
Jolly, J. Amcr. Chem. Soc., 88, 5439 (1966) indicate a pK, of roughly 27-28 for aniline and 28-29
for 4-methylaniline. pK, of 4-nitroaniline is about 18 (Ref. 12).
14. W. K. McEwen, J. Amr. Chem. Soc., 58, 1124 (1936).
15. F. G. Bordwell, R. H. Imes, and E. C. Steiner, J. Amr. Chem. Soc., 89, 3905 (1967).
16. R. Stewart and J. R. Jones, J. Amr. Chem. Soc., 89, 5069 (1967).