Page 232 - Mechanism and Theory in Organic Chemistry
P. 232
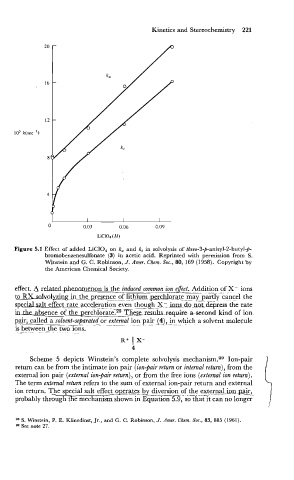
Kinetics and Stereochemistry 221
LC104 (M)
Figure 5.1 Effect of added LiClO, on k, and kt in solvolysis of threo-3-p-anisyl-2-butyl-p-
bromobenzenesulfonate (3) in acetic acid. Reprinted with permission from S.
Winstein and G. C. Robinson, J. Amer. Chem. Soc., 80, 169 (1958). Copyright by
the American Chemical Society.
effect. A r-enon is the induced common ion efect. Addition of X- ions
-- -- .- -. . . . .
-
t~~)lsalvol.~i~ghkgesenceoflithium~~p~rzhl~ra_t_e_may-p~~y
the
cancel
spd salt effect rate acceleration even though-X.~ianS4~~ot.depres rate
the
in_the absence of the perchlorate? Thescsesuk-xquireea-second kind of ion.
pair, called a solvent-separated or external ion pair (41, in which a solvent molecule
--
_ A_~.~.. . - - .
.-
-
is between-!he -~... tgions.
~.
~
Scheme 5 depicts Winstein's complete solvolysis mechanism.29 Ion-pair
return can be from the intimate ion pair (ion-pair return or internal return), from the
external ion pair (external ion-pair return), or from the free ions (external ion return).
The term external return refers to the sum of external ion-pair return and external
ion return. The special salt effect opergtes by diversion of the exterggl-bn qai5,-
- - - -- - - - -
- -
probably thrzugh the mechanism shown in Equation 5.9, so that it can no longer I
28 S. Winstein, P. E. Klinedinst, Jr., and G. C. Robinson, J. Amer. Chem. SOC., 83, 885 (1961).
28 See note 27.