Page 389 - Mechanism and Theory in Organic Chemistry
P. 389
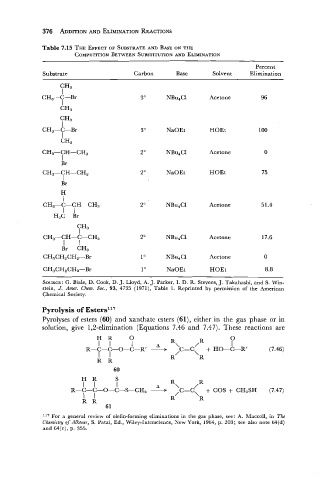
376 ADDI'TION AND ELIMINATION REACTIONS
Table 7.15 THE EFFECT OF SUBSTRATE AND BASE ON THE
COMPETITION BETWEEN SUBSTITUTION AND ELIMINATION
Percent
Substrate Carbon Base Solvent Elimination
Acetone
NaOEt HOEt
NBu4CI Acetone
NaOEt HOEt
Acetone
Acetone
NBu4C1 Acetone
NaOEt HOEt
SOURCE: G. Biale, D. Cook, D. J. Lloyd, A. J. Parker, I. D. R. Stevens, J. Takahashi, and S. Win-
stein, J. Amer. Cham. SOC., 93, 4735 (1971), Table 1. Reprinted by permission of the American
Chemical Society.
Pyrolysis of Esters117
Pyrolyses of esters (60) and xanthate esters (61), either in the gas phase or in
solution, give 1,2-elimination (Equations 7.46 and 7.47). These reactions are
H R 0 R R 0
I I I1 A \ / II
R-C-C-0-C-R' + /C=C + HO-C-R' (7.4'5)
I I R \
R
R R
60
H R S R R
I I I I A \ /
R-C-C-0-C--S-CH3 + /C=C + COS + CH3SH (7.47)
I I R \
R
R R
6 1
For a general review of olefin-forming eliminations in the gas phase, see: A. Maccoll, in The
Chemistry of Alkanes, S. Patai, Ed., Wiley-Interscience, New York, 1964, p. 203; see also note 64(d)
and 64(e), p. 355.