Page 142 - Mechatronics for Safety, Security and Dependability in a New Era
P. 142
Ch26-I044963.fm Page 126 Tuesday, August 1, 2006 3:00 PM
Ch26-I044963.fm
126
126 Page 126 Tuesday, August 1, 2006 3:00 PM
fixture except for Kimura and Yashima's one can fix any work rigidly but cannot correct the position
error occurring at the contact with the work because it is adaptive surface-fitting type. On the other
hand, Kimura and Yashima's fixture can correct the position error but is hard to fix a work rigidly.
Therefore we developed "active flexible fixture (AFLEF)" that can fix any work rigidly and actively
by only position control and also position the fixed work at a few millimeters in order to correct the
location of fixing point into the assembling point. This paper describes the AFLEF on plane level as a
prototype and the performance of each function.
2. PROTOTYPE OF THE AFLEF
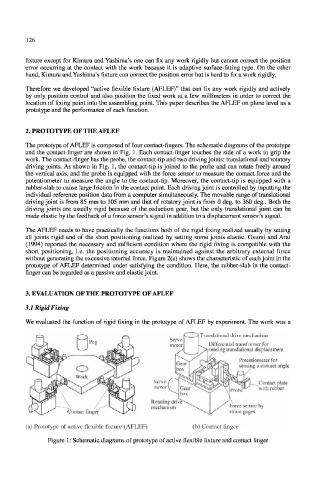
The prototype of AFLEF is composed of four contact-fingers. The schematic diagrams of the prototype
and the contact-finger are shown in Fig. 1. Each contact-finger touches the side of a work to grip the
work. The contact-finger has the probe, the contact-tip and two driving joints: translational and rotatory
driving joints. As shown in Fig. 1, the contact-tip is joined to the probe and can rotate freely around
the vertical axis, and the probe is equipped with the force sensor to measure the contact force and the
potentiometer to measure the angle to the contact-tip. Moreover, the contact-tip is equipped with a
rubber-slab to cause large friction in the contact point. Each driving joint is controlled by inputting the
individual reference position data from a computer simultaneously. The movable range of translational
driving joint is from 85 mm to 105 mm and that of rotatory joint is from 0 deg. to 360 deg.. Both the
driving joints are usually rigid because of the reduction gear, but the only translational joint can be
made elastic by the feedback of a force sensor's signal in addition to a displacement sensor's signal.
The AFLEF needs to have practically the functions both of the rigid fixing realized usually by setting
all joints rigid and of the short positioning realized by setting some joints elastic. Osumi and Arai
(1994) reported the necessary and sufficient condition where the rigid fixing is compatible with the
short positioning, i.e. the positioning accuracy is maintained against the arbitrary external force
without generating the excessive internal force. Figure 2(a) shows the characteristic of each joint in the
prototype of AFLEF determined under satisfying the condition. Here, the rubber-slab in the contact-
finger can be regarded as a passive and elastic joint.
3. EVALUATION OF THE PROTOTYPE OF AFLEF
3.1 Rigid Fixing
We evaluated the function of rigid fixing in the prototype of AFLEF by experiment. The work was a
Translational drive mechanism
Differential transformer for
sensing translational displacement
Potentiometer for
sensing a contact angle
Contact plate
with rubber
Rotating drive
mechanism Force sensor by
Contact finger strain gages
(a) Prototype of active flexible fixture (AFLEF) (b) Contact finger
Figure 1: Schematic diagrams of prototype of active flexible fixture and contact finger