Page 368 - Mechatronics for Safety, Security and Dependability in a New Era
P. 368
Ch71-I044963.fm Page 352 Tuesday, August 1, 2006 4:45 PM
Ch71-I044963.fm
352
352 Page 352 Tuesday, August 1, 2006 4:45 PM
APPENDIX
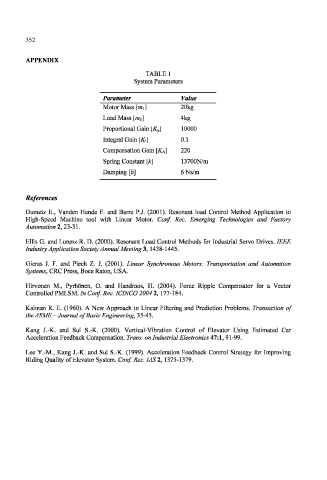
TABLE 1
System Parameters
Parameter Value
Motor Mass [mi] 20kg
Load Mass [m 2] 4kg
Proportional Gain [K v] 10000
Integral Gain [K[] 0.1
Compensation Gain [KA] 220
Spring Constant [k] 13700N/m
Damping [b] 6Ns/m
References
Dumetz E., Vanden Hende F. and Barre P.J. (2001). Resonant load Control Method Application to
High-Speed Machine tool with Linear Motor. Conf. Rec. Emerging Technologies and Factory
Automation 2, 23-31.
Ellis G. and Lorenz R. D. (2000). Resonant Load Control Methods for Industrial Servo Drives. IEEE
Industry Application Society Annual Meeting 3, 1438-1445.
Gieras J. F. and Piech Z. J. (2001). Linear Synchronous Motors: Transportation and Automation
Systems, CRC Press, Boca Raton, USA.
Hirvonen M., Pyrhonen, O. and Handroos, H. (2004). Force Ripple Compensator for a Vector
Controlled PMLSM. In Conf. Rec. 1C1NCO 2004 2, 177-184.
Kalman R. E. (1960). A New Approach to Linear Filtering and Prediction Problems. Transaction of
the ASME - Journal of Basic Engineering, 35-45.
Kang J.-K. and Sul S.-K. (2000). Vertical-Vibration Control of Elevator Using Estimated Car
Acceleration Feedback Compensation. Trans, on Industrial Electronics 47:1, 91-99.
Lee Y.-M., Kang J.-K. and Sul S.-K. (1999). Acceleration Feedback Control Strategy for Improving
Riding Quality of Elevator System. Conf. Rec. IAS 2, 1375-1379.