Page 129 -
P. 129
3.4 Applications of Optical Tweezers 119
Light guide
CCD camera
Mirror G.M.
Filter Axis
Half mirror Filter Eyeplece
Lens alignment
Expander plates
G.M.
G.M.
Dichroic mirror
Movement
Half mirror Iris
Mirror ND filter G.M.
Mirror Movement Dichroic mirror
Quater-wave plate Expander Pinhole
Lens Objective lens
Ar laser for assembly Mirror Specimen
(l = 514.5 nm) plane
Mirror
Objective lens
Filter
Quater-wave plate Fillter
CCD camera
YAG laser for adhesion (l = 355 nm)
(l = 355 nm)
Mirror
Iris
Illuminator
Filter
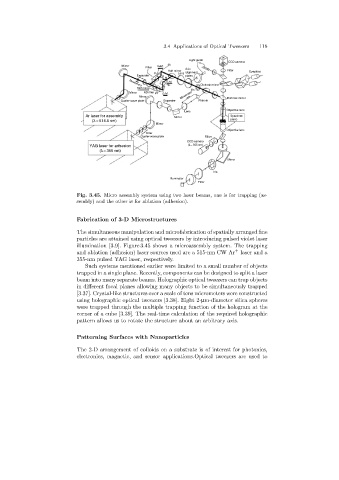
Fig. 3.45. Micro assembly system using two laser beams, one is for trapping (as-
sembly)and the other is for ablation (adhesion).
Fabrication of 3-D Microstructures
The simultaneous manipulation and microfabrication of spatially arranged fine
particles are attained usingoptical tweezers by introducingpulsed violet laser
illumination [3.9]. Figure 3.45 shows a microassembly system. The trapping
+
and ablation (adhesion) laser sources used are a 515-nm CW Ar laser and a
355-nm pulsed YAG laser, respectively.
Such systems mentioned earlier were limited to a small number of objects
trapped in a single plane. Recently, components can be designed to split a laser
beam into many separate beams. Holographic optical tweezers can trap objects
in different focal planes allowingmany objects to be simultaneously trapped
[3.37]. Crystal-like structures over a scale of tens micrometers were constructed
using holographic optical tweezers [3.38]. Eight 2-µm-diameter silica spheres
were trapped through the multiple trapping function of the hologram at the
corner of a cube [3.39]. The real-time calculation of the required holographic
pattern allows us to rotate the structure about an arbitrary axis.
Patterning Surfaces with Nanoparticles
The 2-D arrangement of colloids on a substrate is of interest for photonics,
electronics, magnetic, and sensor applications.Optical tweezers are used to