Page 19 -
P. 19
8 1 From Optical MEMS to Micromechanical Photonics
2R
Lens
f
2romin x
w
v
L
Liquid
y
photopolymer
Solid
z
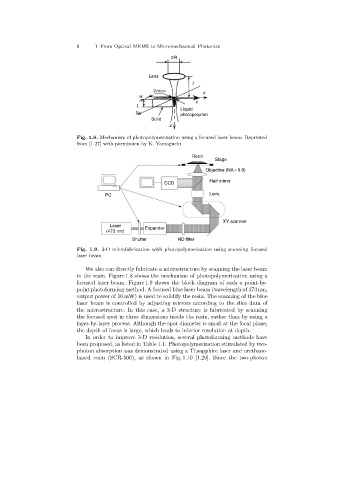
Fig. 1.8. Mechanism of photopolymerization using a focused laser beam. Reprinted
from [1.27] with permission by K. Yamaguchi
Resin
Stage
Objective (NA = 0.8)
Half mirror
CCD
PC Lens
XY scanner
Laser
(473 nm) Expander
Shutter ND filter
Fig. 1.9. 3-D microfabrication with photopolymerization using scanning focused
laser beam
We also can directly fabricate a microstructure by scanningthe laser beam
in the resin. Figure 1.8 shows the mechanism of photopolymerization using a
focused laser beam. Figure 1.9 shows the block diagram of such a point-by-
point photoformingmethod. A focused blue laser beam (wavelength of 473 nm,
output power of 10 mW) is used to solidify the resin. The scanningof the blue
laser beam is controlled by adjustingmirrors accordingto the slice data of
the microstructure. In this case, a 3-D structure is fabricated by scanning
the focused spot in three dimensions inside the resin, rather than by usinga
layer-by-layer process. Although the spot diameter is small at the focal plane,
the depth of focus is large, which leads to inferior resolution at depth.
In order to improve 3-D resolution, several photoformingmethods have
been proposed, as listed in Table 1.1. Photopolymerization stimulated by two-
photon absorption was demonstrated usinga Ti:sapphire laser and urethane-
based resin (SCR-500), as shown in Fig. 1.10 [1.29]. Since the two-photon