Page 204 -
P. 204
194 5 Near Field
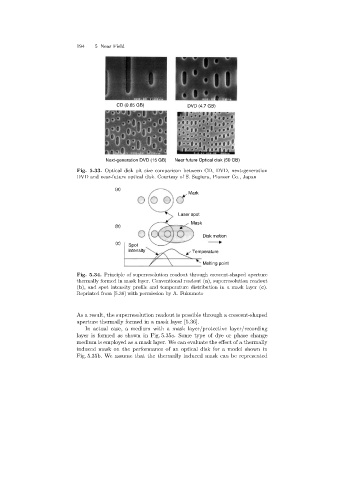
CD (0.65 GB) DVD (4.7 GB)
Next-generation DVD (15 GB) Near future Optical disk (50 GB)
Fig. 5.33. Optical disk pit size comparison between CD, DVD, next-generation
DVD and near-future optical disk. Courtesy of S. Sugiura, Pioneer Co., Japan
(a)
Mark
Laser spot
Mask
(b)
Disk motion
(c)
Spot
intensity Temperature
Melting point
Fig. 5.34. Principle of superresolution readout through crescent-shaped aperture
thermally formed in mask layer. Conventional readout (a), superresolution readout
(b), and spot intensity profile and temperature distribution in a mask layer (c).
Reprinted from [5.36] with permission by A. Fukumoto
As a result, the superresolution readout is possible through a crescent-shaped
aperture thermally formed in a mask layer [5.36].
In actual case, a medium with a mask layer/protective layer/recording
layer is formed as shown in Fig. 5.35a. Some type of dye or phase change
medium is employed as a mask layer. We can evaluate the effect of a thermally
induced mask on the performance of an optical disk for a model shown in
Fig. 5.35b. We assume that the thermally induced mask can be represented