Page 226 -
P. 226
6 Answers, Hints and Solutions 217
output P 1 (PD side) differs from P 2 (medium side). The light output ratio for
a complex cavity laser is calculated usingeffective reflectivity R eff instead of
2
laser facet reflectivity R 2 , as shown [2.34]
eff
1 − R
P 2 R 1 2
= eff .
R (1 − R 1 )
P 1 2
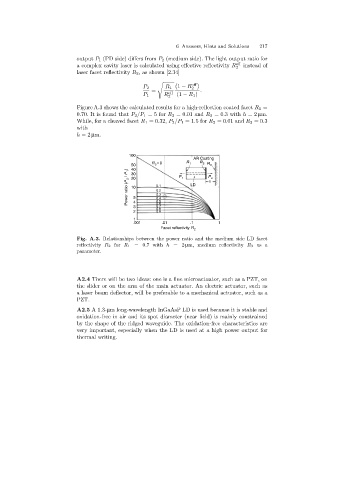
Figure A.3 shows the calculated results for a high-reflection coated facet R 1 =
0.70. It is found that P 2 /P 1 =5 for R 2 =0.01 and R 3 =0.3 with h =2 µm.
While, for a cleaved facet R 1 =0.32, P 2 /P 1 =1.5for R 2 =0.01 and R 3 =0.3
with
h =2 µm.
100
AR Coating
R =0 R R 2 R
50 3 1 3
40
Power ratio (P 2 / P 1 ) 20 0.1 P 1 LD P h 2
30
10
0.2
0.3
0.5
0.6
0.7
3 5 4 0.4
0.8
2 0.9
1
.001 .01 .1 1
Facet reflectivity R 2
Fig. A.3. Relationships between the power ratio and the medium side LD facet
reflectivity R 2 for R 1 =0.7with h =2 µm, medium reflectivity R 3 as a
parameter.
A2.4 There will be two ideas: one is a fine microactuator, such as a PZT, on
the slider or on the arm of the main actuator. An electric actuator, such as
a laser beam deflector, will be preferable to a mechanical actuator, such as a
PZT.
A2.5 A 1.3-µm long-wavelength InGaAsP LD is used because it is stable and
oxidation-free in air and its spot diameter (near field) is mainly constrained
by the shape of the ridged waveguide. The oxidation-free characteristics are
very important, especially when the LD is used at a high power output for
thermal writing.