Page 33 -
P. 33
22 1 From Optical MEMS to Micromechanical Photonics
Light output
Ti/W
Mirror
V
Support
Common
electrode
MQWs
Bragg mirror
I
Bonding GaAs substrate bias
layer
Back side contact
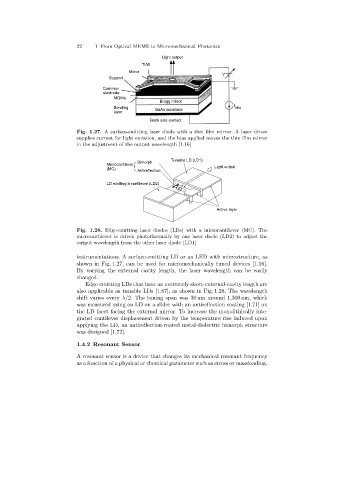
Fig. 1.27. A surface-emitting laser diode with a thin film mirror. A laser driver
supplies current for light emission, and the bias applied moves the thin film mirror
in the adjustment of the output wavelength [1.16]
Tunable LD (LD1)
Bimorph
Microcantilever
(MC) Antireflection Light output
LD exciting a cantilever (LD2)
Active layer
Fig. 1.28. Edge-emitting laser diodes (LDs)with a microcantilever (MC). The
microcantilever is driven photothermally by one laser diode (LD2)to adjust the
output wavelength from the other laser diode (LD1)
instrumentations. A surface-emittingLD or an LED with microstructure, as
shown in Fig. 1.27, can be used for micromechanically tuned devices [1.16].
By varying the external cavity length, the laser wavelength can be easily
changed.
Edge-emitting LDs that have an extremely short-external-cavity length are
also applicable as tunable LDs [1.67], as shown in Fig. 1.28. The wavelength
shift varies every λ/2. The tuningspan was 30 nm around 1,300 nm, which
was measured usingan LD on a slider with an antireflection coating[1.71] on
the LD facet facingthe external mirror. To increase the monolithically inte-
grated cantilever displacement driven by the temperature rise induced upon
applyingthe LD, an antireflection-coated metal-dielectric bimorph structure
was designed [1.72].
1.4.2 Resonant Sensor
A resonant sensor is a device that changes its mechanical resonant frequency
as a function of a physical or chemical parameter such as stress or massloading.