Page 36 -
P. 36
1.4 Integrated Systems with LDs and Micromechanics 25
Ridged waveguide
LD
PD
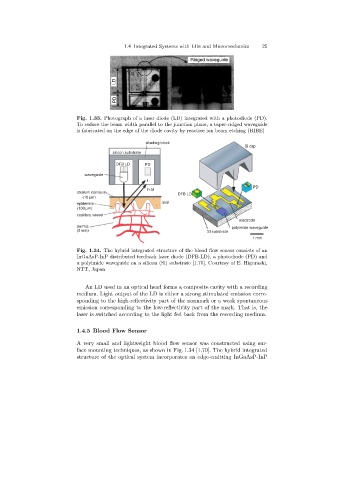
Fig. 1.33. Photograph of a laser diode (LD)integrated with a photodiode (PD).
To reduce the beam width parallel to the junction plane, a taper-ridged waveguide
is fabricated on the edge of the diode cavity by reactive ion beam etching (RIBE)
shading block
Si cap
silicon substrate
DFB LD PD
waveguide
f
PD
f+Df
stratum corneum
DFB LD
(10 mm)
epidermis skin
(100 mm)
capillary vessel
electrode
dermis polyimide waveguide
(3 mm) Si substrate
1mm
Fig. 1.34. The hybrid integrated structure of the blood flow sensor consists of an
InGaAsP-InP distributed feedback laser diode (DFB-LD), a photodiode (PD) and
a polyimide waveguide on a silicon (Si)substrate [1.70]. Courtesy of E. Higurashi,
NTT, Japan
An LD used in an optical head forms a composite cavity with a recording
medium. Light output of the LD is either a strong stimulated emission corre-
spondingto the high-reflectivity part of the nonmark or a weak spontaneous
emission correspondingto the low-reflectivity part of the mark. That is, the
laser is switched accordingto the light fed back from the recordingmedium.
1.4.5 Blood FlowSensor
A very small and lightweight blood flow sensor was constructed using sur-
face mounting techniques, as shown in Fig. 1.34 [1.70]. The hybrid integrated
structure of the optical system incorporates an edge-emitting InGaAsP-InP