Page 74 -
P. 74
2.4 Applications 63
10 -2
Experimental
Theoretical
10 -3
Reflectivity
10 -4
10 -5
1.75 1.80 1.85 1.90 1.95
Refractive index
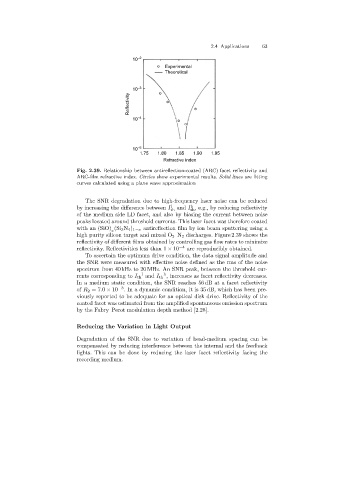
Fig. 2.39. Relationship between antireflection-coated (ARC)facet reflectivity and
ARC-film refractive index. Circles show experimental results. Solid lines are fitting
curves calculated using a plane wave approximation
The SNR degradation due to high-frequency laser noise can be reduced
h
by increasingthe difference between I l and I , e.g., by reducing reflectivity
th th
of the medium side LD facet, and also by biasingthe current between noise
peaks located around threshold currents. This laser facet was therefore coated
with an (SiO) (Si 3 N 4 ) 1−x antireflection film by ion beam sputteringusinga
x
high purity silicon target and mixed O 2 –N 2 discharges. Figure 2.39 shows the
reflectivity of different films obtained by controllinggas flow rates to minimize
reflectivity. Reflectivities less than 1 × 10 −4 are reproducibly obtained.
To ascertain the optimum drive condition, the data signal amplitude and
the SNR were measured with effective noise defined as the rms of the noise
spectrum from 40 kHz to 20 MHz. An SNR peak, between the threshold cur-
h
l
rents correspondingto I th and I th , increases as facet reflectivity decreases.
In a medium static condition, the SNR reaches 56 dB at a facet reflectivity
of R 2 =7.0 × 10 −3 . In a dynamic condition, it is 35 dB, which has been pre-
viously reported to be adequate for an optical disk drive. Reflectivity of the
coated facet was estimated from the amplified spontaneous emission spectrum
by the Fabry–Perot modulation depth method [2.28].
Reducing the Variation in Light Output
Degradation of the SNR due to variation of head-medium spacing can be
compensated by reducinginterference between the internal and the feedback
lights. This can be done by reducing the laser facet reflectivity facing the
recordingmedium.