Page 69 -
P. 69
58 2 Extremely Short-External-Cavity Laser Diode
2.4.3 Optically Switched Laser Head
In this section a small flyingoptical head and its high quality readout charac-
teristics when used as an optically switched laser (OSL) head are described.
The basic concept involved the use of light emitted and collected through
a1-µm diameter aperture of an LD placed less than 2 µm from a recording
medium (ESEC LD configuration). For autofocus, the head operates like a
magnetic head: air-bearing technology stabilizes the slider flying height ap-
proximately 1 µm as shown in Fig. 2.32. Controlled by a sampled servo track
error signal, the arm used to seek from track to track is also used for track
followingas described later.
Drive Structure
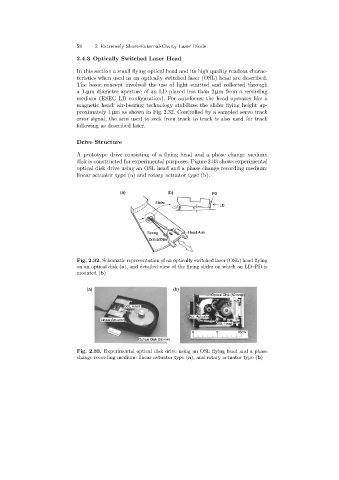
A prototype drive consistingof a flyinghead and a phase change medium
disk is constructed for experimental purposes. Figure 2.33 shows experimental
optical disk drive usingan OSL head and a phase change recordingmedium:
linear actuator type (a) and rotary actuator type (b).
(a) (b) PD
Slider
LD
h
Spring Head Arm
Optical Disk
Fig. 2.32. Schematic representation of an optically switched laser (OSL)head flying
on an optical disk (a), and detailed view of the flying slider on which an LD–PD is
mounted (b)
(a) (b)
Optical Disk (50 mmf)
OSL Head
Rot. Actuator
Linear Actuator
OSL Head
0 5 10cm
Optical Disk (86 mm)
Fig. 2.33. Experimental optical disk drive using an OSL flying head and a phase
change recording medium: linear actuator type (a), and rotary actuator type (b)