Page 88 -
P. 88
2.5 Designs for Related Problems of an ESEC LD 77
Flying height
Beam diam h = 2mm LD slider attached error
Protective layer thickness
Read SNR R = 0.01
2
eff
R 2
Write-erase power margin
LD efficiency R 3 Medium sensitivity
Permissible read power
R 1
PD sensitivity
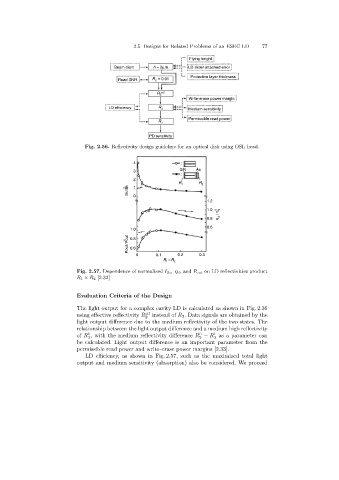
Fig. 2.56. Reflectivity design guideline for an optical disk using OSL head.
4
3 SiN Au
2
R 1 R 2
Ith/Ith 0
o 1
1.2
1.0
/ o p p
0.8
0.6
1.0
Pout/Pout 0.6
o 0.8
0 0.1 0.2 0.3
R R 2
1
Fig. 2.57. Dependence of normalized I th,η d,and P out on LD reflectivities product
R 1 × R 2 [2.32]
Evaluation Criteria of the Design
The light output for a complex cavity LD is calculated as shown in Fig. 2.36
usingeffective reflectivity R eff instead of R 2 . Data signals are obtained by the
2
light output difference due to the medium reflectivity of the two states. The
relationship between the light output difference and a medium high reflectivity
h
l
h
of R , with the medium reflectivity difference R − R as a parameter can
3 3 3
be calculated. Light output difference is an important parameter from the
permissible read power and write–erase power margins [2.33].
LD efficiency, as shown in Fig. 2.57, such as the maximized total light
output and medium sensitivity (absorption) also be considered. We proceed