Page 314 - A Practical Guide from Design Planning to Manufacturing
P. 314
284 Chapter Nine
Serif
+90°
Cutout
Side
rigger
Hammer
head
−90° −90°
Conventional With OPC With OPC and PSM
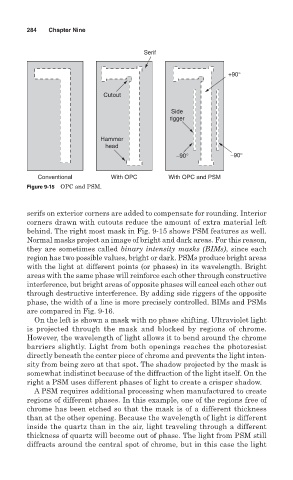
Figure 9-15 OPC and PSM.
serifs on exterior corners are added to compensate for rounding. Interior
corners drawn with cutouts reduce the amount of extra material left
behind. The right most mask in Fig. 9-15 shows PSM features as well.
Normal masks project an image of bright and dark areas. For this reason,
they are sometimes called binary intensity masks (BIMs), since each
region has two possible values, bright or dark. PSMs produce bright areas
with the light at different points (or phases) in its wavelength. Bright
areas with the same phase will reinforce each other through constructive
interference, but bright areas of opposite phases will cancel each other out
through destructive interference. By adding side riggers of the opposite
phase, the width of a line is more precisely controlled. BIMs and PSMs
are compared in Fig. 9-16.
On the left is shown a mask with no phase shifting. Ultraviolet light
is projected through the mask and blocked by regions of chrome.
However, the wavelength of light allows it to bend around the chrome
barriers slightly. Light from both openings reaches the photoresist
directly beneath the center piece of chrome and prevents the light inten-
sity from being zero at that spot. The shadow projected by the mask is
somewhat indistinct because of the diffraction of the light itself. On the
right a PSM uses different phases of light to create a crisper shadow.
A PSM requires additional processing when manufactured to create
regions of different phases. In this example, one of the regions free of
chrome has been etched so that the mask is of a different thickness
than at the other opening. Because the wavelength of light is different
inside the quartz than in the air, light traveling through a different
thickness of quartz will become out of phase. The light from PSM still
diffracts around the central spot of chrome, but in this case the light