Page 276 - Microsensors, MEMS and Smart Devices - Gardner Varadhan and Awadelkarim
P. 276
256 MICROSENSORS
Vertical
motion
Lateral
Cantilever
beam
Pick up
plate
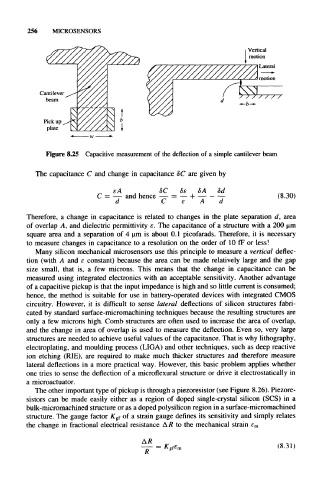
Figure 8.25 Capacitive measurement of the deflection of a simple cantilever beam
The capacitance C and change in capacitance SC are given by
sA 8C Se SA 8d
C = — and hence — = 1 (8.30)
d C e A d
Therefore, a change in capacitance is related to changes in the plate separation d, area
of overlap A, and dielectric permittivity e. The capacitance of a structure with a 200 urn
square area and a separation of 4 urn is about 0.1 picofarads. Therefore, it is necessary
to measure changes in capacitance to a resolution on the order of 10 fF or less!
Many silicon mechanical microsensors use this principle to measure a vertical deflec-
tion (with A and e constant) because the area can be made relatively large and the gap
size small, that is, a few microns. This means that the change in capacitance can be
measured using integrated electronics with an acceptable sensitivity. Another advantage
of a capacitive pickup is that the input impedance is high and so little current is consumed;
hence, the method is suitable for use in battery-operated devices with integrated CMOS
circuitry. However, it is difficult to sense lateral deflections of silicon structures fabri-
cated by standard surface-micromachining techniques because the resulting structures are
only a few microns high. Comb structures are often used to increase the area of overlap,
and the change in area of overlap is used to measure the deflection. Even so, very large
structures are needed to achieve useful values of the capacitance. That is why lithography,
electroplating, and moulding process (LIGA) and other techniques, such as deep reactive
ion etching (RIE), are required to make much thicker structures and therefore measure
lateral deflections in a more practical way. However, this basic problem applies whether
one tries to sense the deflection of a microflexural structure or drive it electrostatically in
a microactuator.
The other important type of pickup is through a piezoresistor (see Figure 8.26). Piezore-
sistors can be made easily either as a region of doped single-crystal silicon (SCS) in a
bulk-micromachined structure or as a doped polysilicon region in a surface-micromachined
structure. The gauge factor K gf of a strain gauge defines its sensitivity and simply relates
the change in fractional electrical resistance A/? to the mechanical strain e m
AR
— (8.31)