Page 230 - Modern Analytical Chemistry
P. 230
1400-CH07 9/8/99 4:04 PM Page 213
Chapter 7 Obtaining and Preparing Samples for Analysis 213
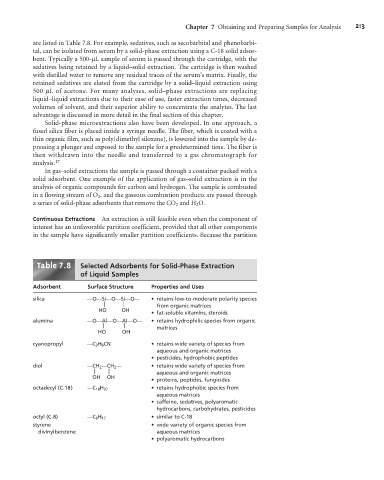
are listed in Table 7.8. For example, sedatives, such as secobarbital and phenobarbi-
tal, can be isolated from serum by a solid-phase extraction using a C-18 solid adsor-
bent. Typically a 500-mL sample of serum is passed through the cartridge, with the
sedatives being retained by a liquid–solid extraction. The cartridge is then washed
with distilled water to remove any residual traces of the serum’s matrix. Finally, the
retained sedatives are eluted from the cartridge by a solid–liquid extraction using
500 mL of acetone. For many analyses, solid–phase extractions are replacing
liquid–liquid extractions due to their ease of use, faster extraction times, decreased
volumes of solvent, and their superior ability to concentrate the analytes. The last
advantage is discussed in more detail in the final section of this chapter.
Solid-phase microextractions also have been developed. In one approach, a
fused silica fiber is placed inside a syringe needle. The fiber, which is coated with a
thin organic film, such as poly(dimethyl siloxane), is lowered into the sample by de-
pressing a plunger and exposed to the sample for a predetermined time. The fiber is
then withdrawn into the needle and transferred to a gas chromatograph for
analysis. 17
In gas–solid extractions the sample is passed through a container packed with a
solid adsorbent. One example of the application of gas–solid extraction is in the
analysis of organic compounds for carbon and hydrogen. The sample is combusted
in a flowing stream of O 2 , and the gaseous combustion products are passed through
a series of solid-phase adsorbents that remove the CO 2 and H 2 O.
Continuous Extractions An extraction is still feasible even when the component of
interest has an unfavorable partition coefficient, provided that all other components
in the sample have significantly smaller partition coefficients. Because the partition
7
Table .8 Selected Adsorbents for Solid-Phase Extraction
of Liquid Samples
Adsorbent Surface Structure Properties and Uses
silica —O—Si—O—Si—O— • retains low-to-moderate polarity species
| | from organic matrices
HO OH
• fat-soluble vitamins, steroids
alumina —O—Al—O—Al—O— • retains hydrophilic species from organic
| | matrices
HO OH
cyanopropyl —C 3 H 6 CN • retains wide variety of species from
aqueous and organic matrices
• pesticides, hydrophobic peptides
diol —CH 2 —CH 2 — • retains wide variety of species from
| | aqueous and organic matrices
OH OH
• proteins, peptides, fungicides
octadecyl (C-18) —C 18 H 37 • retains hydrophobic species from
aqueous matrices
• caffeine, sedatives, polyaromatic
hydrocarbons, carbohydrates, pesticides
octyl (C-8) —C 8 H 17 • similar to C-18
styrene • wide variety of organic species from
divinylbenzene aqueous matrices
• polyaromatic hydrocarbons