Page 333 - Modern Analytical Chemistry
P. 333
1400-CH09 9/9/99 2:13 PM Page 316
316 Modern Analytical Chemistry
9 4–
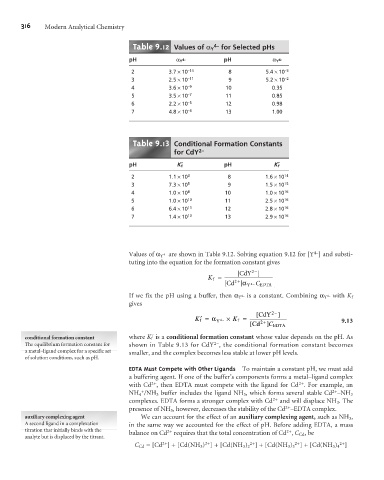
Table .12 Values of a Y for Selected pHs
pH a Y 4- pH a Y 4-
2 3.7 ´10 –14 8 5.4 ´10 –3
3 2.5 ´10 –11 9 5.2 ´10 –2
4 3.6 ´10 –9 10 0.35
5 3.5 ´10 –7 11 0.85
6 2.2 ´10 –5 12 0.98
7 4.8 ´10 –4 13 1.00
9 3
Table .1 Conditional Formation Constants
for CdY 2–
pH K’ f pH K’ f
2 1.1 ´10 3 8 1.6 ´ 10 14
3 7.3 ´10 5 9 1.5 ´10 15
4 1.0 ´10 8 10 1.0 ´ 10 16
5 1.0 ´10 10 11 2.5 ´10 16
6 6.4 ´10 11 12 2.8 ´10 16
7 1.4 ´10 13 13 2.9 ´10 16
4–
Values of a Y are shown in Table 9.12. Solving equation 9.12 for [Y ] and substi-
4–
tuting into the equation for the formation constant gives
2 -
[ CdY ]
K f =
2 +
[ Cd ]a
Y 4- C EDTA
4–
4–
If we fix the pH using a buffer, then a Y is a constant. Combining a Y with K f
gives
[ CdY 2 - ]
¢= a =
K f 4 - ´K f
Y 2 + 9.13
[ Cd ] C EDTA
conditional formation constant where K f ´ is a conditional formation constant whose value depends on the pH. As
2–
The equilibrium formation constant for shown in Table 9.13 for CdY , the conditional formation constant becomes
a metal–ligand complex for a specific set smaller, and the complex becomes less stable at lower pH levels.
of solution conditions, such as pH.
EDTA Must Compete with Other Ligands To maintain a constant pH, we must add
a buffering agent. If one of the buffer’s components forms a metal–ligand complex
2+
2+
with Cd , then EDTA must compete with the ligand for Cd . For example, an
+ 2+
NH 4 /NH 3 buffer includes the ligand NH 3 , which forms several stable Cd –NH 3
complexes. EDTA forms a stronger complex with Cd 2+ and will displace NH 3 . The
2+
presence of NH 3 , however, decreases the stability of the Cd –EDTA complex.
auxiliary complexing agent We can account for the effect of an auxiliary complexing agent, such as NH 3 ,
A second ligand in a complexation in the same way we accounted for the effect of pH. Before adding EDTA, a mass
titration that initially binds with the 2+ 2+
balance on Cd requires that the total concentration of Cd , C Cd , be
analyte but is displaced by the titrant.
2+
2+
2+
2+
2+
C Cd = [Cd ] + [Cd(NH 3 ) ] + [Cd(NH 3 ) 2 ] + [Cd(NH 3 ) 3 ] + [Cd(NH 3 ) 4 ]