Page 288 - Modern Control Systems
P. 288
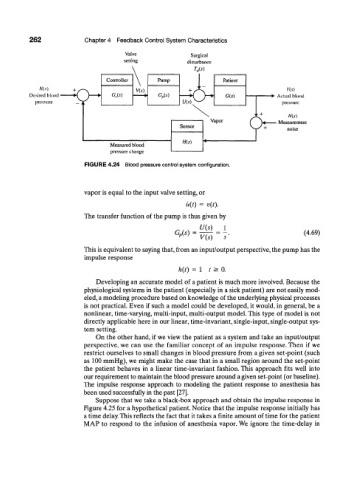
262 Chapter 4 Feedback Control System Characteristics
Valve Surgical
setting disturbance
w
Controller Pump
o-
R(s) \ Y(s)
Desired blood G c(s) G p(s) • Actual blood
pressure pressure
4 Measurement
Measured blood
pressure change
FIGURE 4.24 Blood pressure control system configuration.
vapor is equal to the input valve setting, or
u(t) = v(t).
The transfer function of the pump is thus given by
U(s) 1
GM = (4.69)
V(s)
This is equivalent to saying that, from an input/output perspective, the pump has the
impulse response
h{t) = 1 t > 0.
Developing an accurate model of a patient is much more involved. Because the
physiological systems in the patient (especially in a sick patient) are not easily mod-
eled, a modeling procedure based on knowledge of the underlying physical processes
is not practical. Even if such a model could be developed, it would, in general, be a
nonlinear, time-varying, multi-input, multi-output model. This type of model is not
directly applicable here in our linear, time-invariant, single-input, single-output sys-
tem setting.
On the other hand, if we view the patient as a system and take an input/output
perspective, we can use the familiar concept of an impulse response. Then if we
restrict ourselves to small changes in blood pressure from a given set-point (such
as 100 mmHg), we might make the case that in a small region around the set-point
the patient behaves in a linear time-invariant fashion. This approach fits well into
our requirement to maintain the blood pressure around a given set-point (or baseline).
The impulse response approach to modeling the patient response to anesthesia has
been used successfully in the past [27].
Suppose that we take a black-box approach and obtain the impulse response in
Figure 4.25 for a hypothetical patient. Notice that the impulse response initially has
a time delay. This reflects the fact that it takes a finite amount of time for the patient
MAP to respond to the infusion of anesthesia vapor. We ignore the time-delay in