Page 36 - Modern Control of DC-Based Power Systems
P. 36
CHAPTER ONE
Overview—Voltage Stabilization
of Constant Power Loads
Throughout this chapter the reader will be introduced to the characteris-
tics of the Constant Power Load (CPL) while being connected to a DC
bus in Section 1.1. The Sections 1.2 1.4 present an overview on the pre-
vious research activities performed for stabilizing CPLs. Section 1.5 offers
a summary of this chapter.
1.1 CONSTANT POWER LOAD CONNECTED TO A DC
BUS
The interaction of electrical subsystems around a DC bus can lead
to the instability of the latter. Often in these cases, it is associated with
the occurrence of instability when CPLs are connected on the DC bus
[1 14]. The phenomenon of instability is considered then as the conse-
quence of the connection of a CPL on a DC bus.
When there is an element present which regulates the power con-
sumption of a load (e.g., inverter/actuator, converter/battery converter,
drive), it is possible to assume the aforementioned CPL behavior. The
control of the load will then set the load to compensate disturbances on
the bus. The load does not take into account the electrical state of the
network (including DC bus). Thus, it will be seen by the DC bus as a
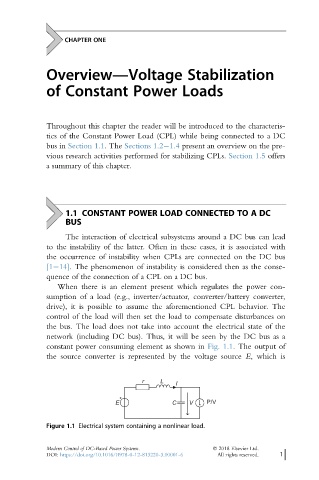
constant power consuming element as shown in Fig. 1.1. The output of
the source converter is represented by the voltage source E, which is
r L
I
E C V P/V
Figure 1.1 Electrical system containing a nonlinear load.
Modern Control of DC-Based Power Systems. © 2018 Elsevier Ltd.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-813220-3.00001-6 All rights reserved. 1