Page 188 - Modern Derivatization Methods for Separation Sciences
P. 188
Document Página 1 de 2
Page 85
Fig. 2.28.
The reaction of hydroxyl group and benzoyl chloride.
alcohols, and the derivatized and purified serum sample was analyzed within 8 min. A typical
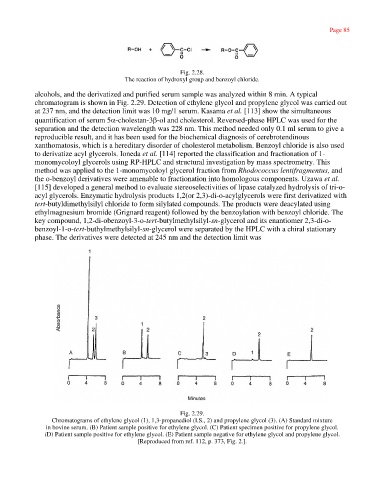
chromatogram is shown in Fig. 2.29. Detection of ethylene glycol and propylene glycol was carried out
at 237 nm, and the detection limit was 10 mg/1 serum. Kasama et al. [113] show the simultaneous
quantification of serum 5α-cholestan-3β-ol and cholesterol. Reversed-phase HPLC was used for the
separation and the detection wavelength was 228 nm. This method needed only 0.1 ml serum to give a
reproducible result, and it has been used for the biochemical diagnosis of cerebrotendinous
xanthomatosis, which is a hereditary disorder of cholesterol metabolism. Benzoyl chloride is also used
to derivatize acyl glycerols. Ioneda et al. [114] reported the classification and fractionation of 1-
monomycoloyl glycerols using RP-HPLC and structural investigation by mass spectrometry. This
method was applied to the 1-monomycoloyl glycerol fraction from Rhodococcus lentifragmentus, and
the o-benzoyl derivatives were amenable to fractionation into homologous components. Uzawa et al.
[115] developed a general method to evaluate stereoselectivities of lipase catalyzed hydrolysis of tri-o-
acyl glycerols. Enzymatic hydrolysis products 1,2(or 2,3)-di-o-acylglycerols were first derivatized with
tert-butyldimethylsilyl chloride to form silylated compounds. The products were deacylated using
ethylmagnesium bromide (Grignard reagent) followed by the benzoylation with benzoyl chloride. The
key compound, 1,2-di-obenzoyl-3-o-tert-butylmethylsilyl-sn-glycerol and its enantiomer 2,3-di-o-
benzoyl-1-o-tert-buthylmethylsilyl-sn-glycerol were separated by the HPLC with a chiral stationary
phase. The derivatives were detected at 245 nm and the detection limit was
Fig. 2.29.
Chromatograms of ethylene glycol (1), 1,3-propanediol (I.S., 2) and propylene glycol (3). (A) Standard mixture
in bovine serum. (B) Patient sample positive for ethylene glycol. (C) Patient specimen positive for propylene glycol.
(D) Patient sample positive for ethylene glycol. (E) Patient sample negative for ethylene glycol and propylene glycol.
[Reproduced from ref. 112, p. 373, Fig. 2.].
http://emedia.netlibrary.com/nlreader/nlreader.dll?bookid=17968&filename=Page_85.html 30/09/2003