Page 199 - Modern Derivatization Methods for Separation Sciences
P. 199
Document Página 1 de 2
Page 91
were separated with CE-CZE (capillary zone electrophoresis) using borate buffer (pH 10.0) as a
electrophoresis buffer. The detection was carried out at 291 nm and the detection limit was 170 fmol.
Calibration range was 10-500 µg/ml. Rydlund et al. [134] showed an efficient CZE separation of wood-
derived saccharides. Carbohydrates released from hemicellulose were derivatized with 6-
aminoquinoline (6-AQ) and cyanoborohydride and separated by CE-CZE as borate complexes within
15 min. Derivatives were monitored at 245 nm and the detection limit was in the few fmol range.
Reductive Amination Application: Determination of Oligosaccharide Derivatized with N-(4-
Aminobenzoyl)-L-glutamic Acid Using CE-CZE [133]
An oligosaccharide sample (up to 2 mg/ml) was mixed with the derivatizing reagent solution (4% N-(4-
aminobenzoyl)-L-glutamic acid 2% cyanoborohydride in 50% acetic acid). The mixture was heated at
90 °C for 2-3 h. After cooling, the sample was diluted appropriately prior to electrophoresis. Separation
of derivatized oligosaccharide was performed using CE-CZE with a fused silica capillary (75 µm i.d. ×
70 cm). The electrophoresis buffer was a 200 mM borate buffer (pH 10.0) and detection was carried out
at 291 nm. The detection limit of maltopentaose was 170 fmol and the calibration range was 10-500
µg/ml.
2.5.2—
1-Phenyl-3-methyl-5-pyrazolone
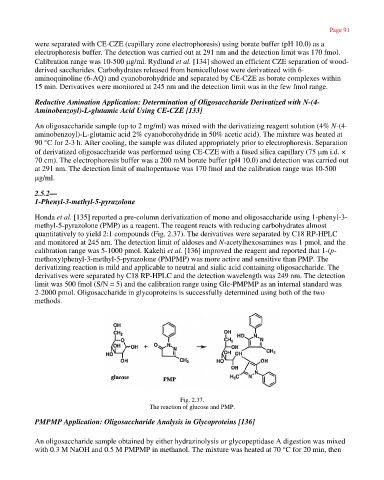
Honda et al. [135] reported a pre-column derivatization of mono and oligosaccharide using 1-phenyl-3-
methyl-5-pyrazolone (PMP) as a reagent. The reagent reacts with reducing carbohydrates almost
quantitatively to yield 2:1 compounds (Fig. 2.37). The derivatives were separated by C18 RP-HPLC
and monitored at 245 nm. The detection limit of aldoses and N-acetylhexosamines was 1 pmol, and the
calibration range was 5-1000 pmol. Kakehi et al. [136] improved the reagent and reported that 1-(p-
methoxy)phenyl-3-methyl-5-pyrazolone (PMPMP) was more active and sensitive than PMP. The
derivatizing reaction is mild and applicable to neutral and sialic acid containing oligosaccharide. The
derivatives were separated by C18 RP-HPLC and the detection wavelength was 249 nm. The detection
limit was 500 fmol (S/N = 5) and the calibration range using Glc-PMPMP as an internal standard was
2-2000 pmol. Oligosaccharide in glycoproteins is successfully determined using both of the two
methods.
Fig. 2.37.
The reaction of glucose and PMP.
PMPMP Application: Oligosaccharide Analysis in Glycoproteins [136]
An oligosaccharide sample obtained by either hydrazinolysis or glycopeptidase A digestion was mixed
with 0.3 M NaOH and 0.5 M PMPMP in methanol. The mixture was heated at 70 °C for 20 min, then
http://emedia.netlibrary.com/nlreader/nlreader.dll?bookid=17968&filename=Page_91.html 30/09/2003