Page 201 - Modern Derivatization Methods for Separation Sciences
P. 201
Document Página 1 de 2
Page 92
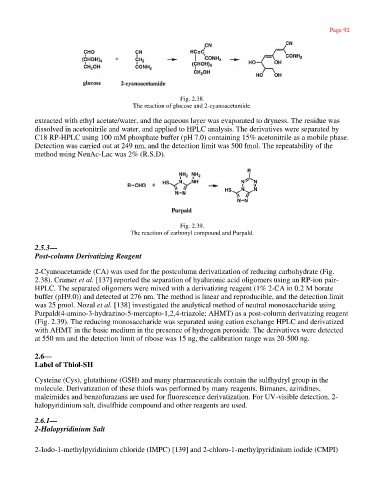
Fig. 2.38.
The reaction of glucose and 2-cyanoacetamide.
extracted with ethyl acetate/water, and the aqueous layer was evaporated to dryness. The residue was
dissolved in acetonitrile and water, and applied to HPLC analysis. The derivatives were separated by
C18 RP-HPLC using 100 mM phosphate buffer (pH 7.0) containing 15% acetonitrile as a mobile phase.
Detection was carried out at 249 nm, and the detection limit was 500 fmol. The repeatability of the
method using NeuAc-Lac was 2% (R.S.D).
Fig. 2.39.
The reaction of carbonyl compound and Purpald.
2.5.3—
Post-column Derivatizing Reagent
2-Cyanoacetamide (CA) was used for the postcolumn derivatization of reducing carbohydrate (Fig.
2.38). Cramer et al. [137] reported the separation of hyaluronic acid oligomers using an RP-ion pair-
HPLC. The separated oligomers were mixed with a derivatizing reagent (1% 2-CA in 0.2 M borate
buffer (pH9.0)) and detected at 276 nm. The method is linear and reproducible, and the detection limit
was 25 pmol. Nozal et al. [138] investigated the analytical method of neutral monosaccharide using
Purpald(4-amino-3-hydrazino-5-mercapto-1,2,4-triazole; AHMT) as a post-column derivatizing reagent
(Fig. 2.39). The reducing monosaccharide was separated using cation exchange HPLC and derivatized
with AHMT in the basic medium in the presence of hydrogen peroxide. The derivatives were detected
at 550 nm and the detection limit of ribose was 15 ng, the calibration range was 20-500 ng.
2.6—
Label of Thiol-SH
Cysteine (Cys), glutathione (GSH) and many pharmaceuticals contain the sulfhydryl group in the
molecule. Derivatization of these thiols was performed by many reagents. Bimanes, aziridines,
maleimides and benzofurazans are used for fluorescence derivatization. For UV-visible detection, 2-
halopyridinium salt, disulfhide compound and other reagents are used.
2.6.1—
2-Halopyridinium Salt
2-Iodo-1-methylpyridinium chloride (IMPC) [139] and 2-chloro-1-methylpyridinium iodide (CMPI)
http://emedia.netlibrary.com/nlreader/nlreader.dll?bookid=17968&filename=Page_92.html 30/09/2003