Page 404 - Multidimensional Chromatography
P. 404
396 Multidimensional Chromatography
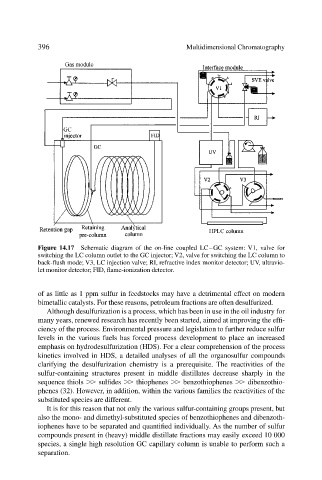
Figure 14.17 Schematic diagram of the on-line coupled LC–GC system: V1, valve for
switching the LC column outlet to the GC injector; V2, valve for switching the LC column to
back-flush mode; V3, LC injection valve; RI, refractive index monitor detector; UV, ultravio-
let monitor detector; FID, flame-ionization detector.
of as little as 1 ppm sulfur in feedstocks may have a detrimental effect on modern
bimetallic catalysts. For these reasons, petroleum fractions are often desulfurized.
Although desulfurization is a process, which has been in use in the oil industry for
many years, renewed research has recently been started, aimed at improving the effi-
ciency of the process. Environmental pressure and legislation to further reduce sulfur
levels in the various fuels has forced process development to place an increased
emphasis on hydrodesulfurization (HDS). For a clear comprehension of the process
kinetics involved in HDS, a detailed analyses of all the organosulfur compounds
clarifying the desulfurization chemistry is a prerequisite. The reactivities of the
sulfur-containing structures present in middle distillates decrease sharply in the
sequence thiols sulfides thiophenes benzothiophenes dibenzothio-
phenes (32). However, in addition, within the various families the reactivities of the
substituted species are different.
It is for this reason that not only the various sulfur-containing groups present, but
also the mono- and dimethyl-substituted species of benzothiophenes and dibenzoth-
iophenes have to be separated and quantified individually. As the number of sulfur
compounds present in (heavy) middle distillate fractions may easily exceed 10 000
species, a single high resolution GC capillary column is unable to perform such a
separation.