Page 192 - Multifunctional Photocatalytic Materials for Energy
P. 192
178 Multifunctional Photocatalytic Materials for Energy
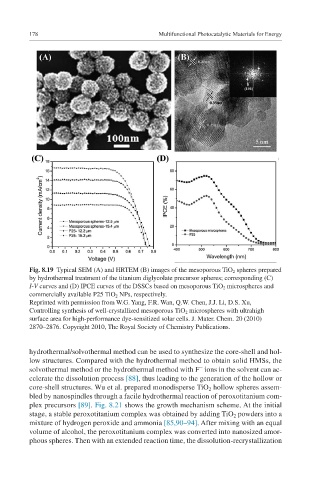
Fig. 8.19 Typical SEM (A) and HRTEM (B) images of the mesoporous TiO 2 spheres prepared
by hydrothermal treatment of the titanium diglycolate precursor spheres; corresponding (C)
I-V curves and (D) IPCE curves of the DSSCs based on mesoporous TiO 2 microspheres and
commercially available P25 TiO 2 NPs, respectively.
Reprinted with permission from W.G. Yang, F.R. Wan, Q.W. Chen, J.J. Li, D.S. Xu,
Controlling synthesis of well-crystallized mesoporous TiO 2 microspheres with ultrahigh
surface area for high-performance dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Mater. Chem. 20 (2010)
2870–2876. Copyright 2010, The Royal Society of Chemistry Publications.
hydrothermal/solvothermal method can be used to synthesize the core-shell and hol-
low structures. Compared with the hydrothermal method to obtain solid HMSs, the
−
solvothermal method or the hydrothermal method with F ions in the solvent can ac-
celerate the dissolution process [88], thus leading to the generation of the hollow or
core-shell structures. Wu et al. prepared monodisperse TiO 2 hollow spheres assem-
bled by nanospindles through a facile hydrothermal reaction of peroxotitanium com-
plex precursors [89]. Fig. 8.21 shows the growth mechanism scheme. At the initial
stage, a stable peroxotitanium complex was obtained by adding TiO 2 powders into a
mixture of hydrogen peroxide and ammonia [85,90–94]. After mixing with an equal
volume of alcohol, the peroxotitanium complex was converted into nanosized amor-
phous spheres. Then with an extended reaction time, the dissolution-recrystallization