Page 126 - Book Hosokawa Nanoparticle Technology Handbook
P. 126
FUNDAMENTALS CH. 2 STRUCTURAL CONTROL OF NANOPARTICLES
1μm 10nm
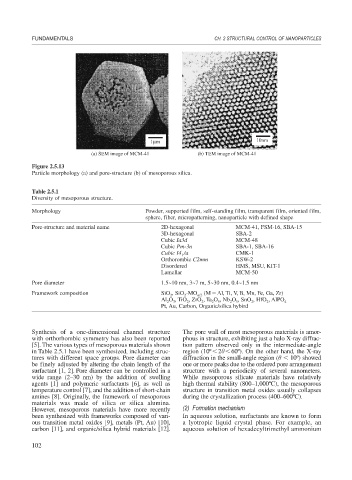
(a) SEM image of MCM-41 (b) TEM image of MCM-41
Figure 2.5.13
Particle morphology (a) and pore-structure (b) of mesoporous silica.
Table 2.5.1
Diversity of mesoporous structure.
Morphology Powder, supported film, self-standing film, transparent film, oriented film,
sphere, fiber, micropatterning, nanoparticle with defined shape
Pore-structure and material name 2D-hexagonal MCM-41, FSM-16, SBA-15
3D-hexagonal SBA-2
Cubic Ia3d MCM-48
Cubic Pm-3n SBA-1, SBA-16
Cubic I4 /a CMK-1
1
Orthorombic C2mm KSW-2
Disordered HMS, MSU, KIT-1
Lamellar MCM-50
Pore diameter 1.5~10 nm, 3~7 m, 5~30 nm, 0.4~1.5 nm
Framework composition SiO , SiO -MO n/2 (M Al, Ti, V, B, Mn, Fe, Ga, Zr)
2
2
Al O , TiO , ZrO , Ta O , Nb O , SnO , HfO , AlPO 4
5
2
5
2
3
2
2
2
2
2
Pt, Au, Carbon, Organic/silica hybird
Synthesis of a one-dimensional channel structure The pore wall of most mesoporous materials is amor-
with orthorhombic symmetry has also been reported phous in structure, exhibiting just a halo X-ray diffrac-
[5]. The various types of mesoporous materials shown tion pattern observed only in the intermediate-angle
in Table 2.5.1 have been synthesized, including struc- region (10º 2 60º). On the other hand, the X-ray
tures with different space groups. Pore diameter can diffraction in the small-angle region ( 10º) showed
be finely adjusted by altering the chain length of the one or more peaks due to the ordered pore arrangement
surfactant [1, 2]. Pore diameter can be controlled in a structure with a periodicity of several nanometers.
wide range (2–30 nm) by the addition of swelling While mesoporous silicate materials have relatively
agents [1] and polymeric surfactants [6], as well as high thermal stability (800–1,000ºC), the mesoporous
temperature control [7], and the addition of short-chain structure in transition metal oxides usually collapses
amines [8]. Originally, the framework of mesoporous during the crystallization process (400–600ºC).
materials was made of silica or silica alumina.
However, mesoporous materials have more recently (2) Formation mechanism
been synthesized with frameworks composed of vari- In aqueous solution, surfactants are known to form
ous transition metal oxides [9], metals (Pt, Au) [10], a lyotropic liquid crystal phase. For example, an
carbon [11], and organic/silica hybrid materials [12]. aqueous solution of hexadecyltrimethyl ammonium
102