Page 127 - Book Hosokawa Nanoparticle Technology Handbook
P. 127
2.5 PORE STRUCTURE FUNDAMENTALS
bromide (C TMABr), one type of surfactant, forms mesoporous material in which a liquid crystal tem-
16
a liquid crystal phase that is hexagonal, cubic, or plate method is used. A self-organized mesostructure
lamellar in structure, depending on the solution is formed by adding an inorganic precursor
conditions. A periodic pore-structure of mesoporous (tetraethoxysilane, for example) to an aqueous solu-
materials is obtained by transferring the structure of tion of a surfactant under appropriate conditions.
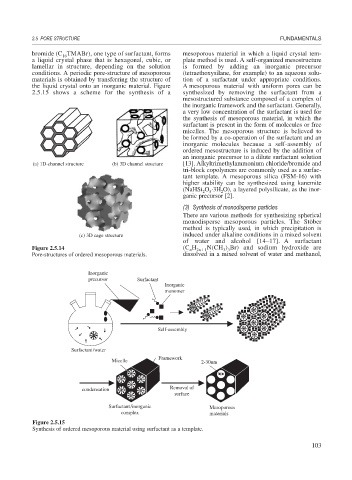
the liquid crystal onto an inorganic material. Figure A mesoporous material with uniform pores can be
2.5.15 shows a scheme for the synthesis of a synthesized by removing the surfactant from a
mesostructured substance composed of a complex of
the inorganic framework and the surfactant. Generally,
a very low concentration of the surfactant is used for
the synthesis of mesoporous material, in which the
surfactant is present in the form of molecules or free
micelles. The mesoporous structure is believed to
be formed by a co-operation of the surfactant and an
inorganic molecules because a self-assembly of
ordered mesostructure is induced by the addition of
an inorganic precursor to a dilute surfactant solution
(a) 1D-channel structure (b) 3D channel structure [13]. Alkyltrimethylammonium chloride/bromide and
tri-block copolymers are commonly used as a surfac-
tant template. A mesoporous silica (FSM-16) with
higher stability can be synthesized using kanemite
(NaHSi O ·3H O), a layered polysilicate, as the inor-
5
2
2
ganic precursor [2].
(3) Synthesis of monodisperse particles
There are various methods for synthesizing spherical
monodisperse mesoporous particles. The Stöber
method is typically used, in which precipitation is
(c) 3D cage structure induced under alkaline conditions in a mixed solvent
of water and alcohol [14–17]. A surfactant
Figure 2.5.14 (C H 2n 1 N(CH ) Br) and sodium hydroxide are
n
3 3
Pore-structures of ordered mesoporous materials. dissolved in a mixed solvent of water and methanol,
Inorganic
precursor Surfactant
Inorganic
monomer
Self-assembly
Surfactant/water
Framework
Micelle 2-30nm
condensation Removal of
surface
Surfactant/inorganic Mesoporous
complex materials
Figure 2.5.15
Synthesis of ordered mesoporous material using surfactant as a template.
103