Page 129 - Book Hosokawa Nanoparticle Technology Handbook
P. 129
2.6 NANOPARTICLE DESIGN FOR DDS FUNDAMENTALS
[16] K. Yano, Y. Fukushima: J. Mater. Chem., 14, 1579–1584 is the active targeting that utilizes the specific affinity
(2004). (e.g. antibody) in human bodies, the other is passive
[17] N. Shimizu, M. Ogawa: Bull. Chem. Soc., Jpn., 78, targeting that is completed by extending the blood-
1154–1159 (2005). circulating time of drug intravenously administered
and increasing the efficiency of drug accumulation in
[18] Q. Huo, J. Feng, F. Schuth and G.D. Stucky: Chem.
the inflammatory region or tumor cells.
Mater., 9, 14–17 (1997).
On the other hand, in considering the concept of
[19] P.J. Bruinsma, A.Y. Kim, J. Liu and S. Baskaran:
DDS as an ideal formulation of drug (DDS in a broad
Chem. Mater., 9, 2507–2512 (1997).
view), it is necessary to focus on delivery of drug
[20] T. Martin, A. Galarneau, F. D. Renzo, F. Fajura and into bodies by selecting the most suitable administra-
D. Plee: Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 41, 2590–2592 (2002). tion route. As a lot of water insoluble drugs have
[21] M. Vallet-Regi, A. Ramila, R.P. del Real and J. Perez- been developed in recent years, it is an important task
Pariente: Chem. Mater., 13, 308–311 (2001). to find the new administration methods in order to
[22] Y.-J. Han, G.D. Stucky and A. Butler: J. Am. Chem. get the certain efficacy of drugs. Although some
Soc., 121, 9897–9898 (1999). drugs are administered restrictedly as injections, it is
preferable for the patient to select the lower invasive
[23] N.K. Mal, M. Fujiwara and Y. Tanaka: Nature, 421,
routes such as an oral administration. It will lead to
350–353 (2003).
the good patient compliance. The demand on devel-
[24] C.-Y. Lai, B.G. Trewyn, D.M. Jeftinija, K. Jeftinija,
opment for this type of dosage forms has been
S. Xu, S. Jeftinija and V.S.-Y. Lin: J. Am. Chem. Soc.,
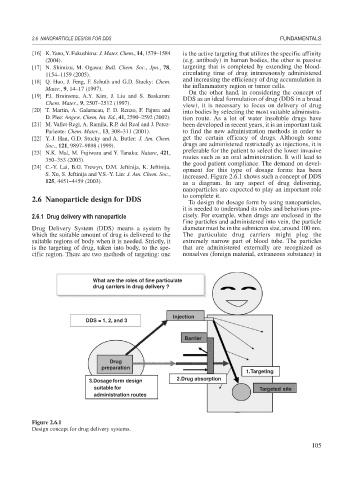
increased. Figure 2.6.1 shows such a concept of DDS
125, 4451–4459 (2003). as a diagram. In any aspect of drug delivering,
nanoparticles are expected to play an important role
to complete it.
2.6 Nanoparticle design for DDS
To design the dosage form by using nanoparticles,
it is needed to understand its roles and behaviors pre-
2.6.1 Drug delivery with nanoparticle cisely. For example, when drugs are enclosed in the
fine particles and administered into vein, the particle
Drug Delivery System (DDS) means a system by diameter must be in the submicron size, around 100 nm.
which the suitable amount of drug is delivered to the The particulate drug carriers might plug the
suitable regions of body when it is needed. Strictly, it extremely narrow part of blood tube. The particles
is the targeting of drug, taken into body, to the spe- that are administered externally are recognized as
cific region. There are two methods of targeting: one nonselves (foreign material, extraneous substance) in
What are the roles of fine particulate
drug carriers in drug delivery ?
Injection
DDS = 1, 2, and 3
Barrier
Drug
preparation
1.Targeting
3.Dosage form design 2.Drug absorption
suitable for Targeted site
administration routes
Figure 2.6.1
Design concept for drug delivery systems.
105