Page 300 - Book Hosokawa Nanoparticle Technology Handbook
P. 300
5.2 CRYSTAL STRUCTURE FUNDAMENTALS
were the TOF neutron powder diffraction instruments
in neutron research facility KENS of KEK as of 2005.
The KENS facility shut down in 2006, however the
successor, whose resolution is much higher, the
range of lattice spacing is much wider, and intensities
are much higher, is under construction at the J-PARC
in Tokai village [2]. Usual measurement requires a
large amount of samples of several cc in volume.
Since the intensity of the incident neutron beam might
be about 100 times more intense in the J-PARC, it will
be easier to collect the neutron diffraction data using
much less quantity of samples. There exist only a few
facilities for neutron diffraction experiments in Japan
and the beam time is limited. Therefore, one should
not utilize neutrons, but X-rays for the subjects one
can study through the X-ray diffraction (XRD).
Next we explain what we know from a diffraction
profile in order to understand the difference between
the neutron and X-ray diffractometry. From the peak
positions, the unit-cell parameters can be determined.
From the peak positions and widths, we can estimate
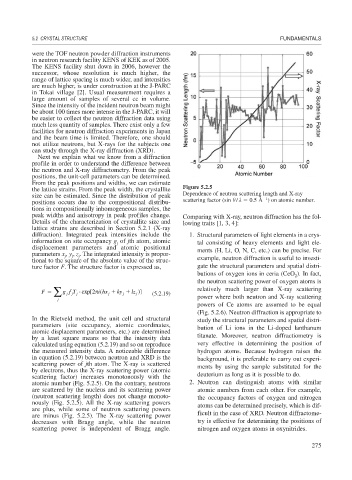
the lattice strains. From the peak width, the crystallite Figure 5.2.5
size can be estimated. Since the distribution of peak Dependence of neutron scattering length and X-ray
1
positions occurs due to the compositional distribu- scattering factor (sin / 0.5 Å ) on atomic number.
tions in compositionally inhomogeneous samples, the
peak widths and anisotropy in peak profiles change. Comparing with X-ray, neutron diffraction has the fol-
Details of the characterization of crystallite size and lowing traits [1, 3, 4]:
lattice strains are described in Section 5.2.1 (X-ray
diffraction). Integrated peak intensities include the 1. Structural parameters of light elements in a crys-
information on site occupancy g of jth atom, atomic tal consisting of heavy elements and light ele-
j
displacement parameters and atomic positional ments (H, Li, O, N, C, etc.) can be precise. For
parameters x , y , z . The integrated intensity is propor-
j
j
j
tional to the square of the absolute value of the struc- example, neutron diffraction is useful to investi-
ture factor F. The structure factor is expressed as, gate the structural parameters and spatial distri-
butions of oxygen ions in ceria (CeO ). In fact,
2
the neutron scattering power of oxygen atoms is
∑ relatively much larger than X-ray scattering
F g f T
exp[2 i hx ky lz )] (5.2.19)
(
j
j j
j
j
j
j power where both neutron and X-ray scattering
powers of Ce atoms are assumed to be equal
(Fig. 5.2.6). Neutron diffraction is appropriate to
In the Rietveld method, the unit cell and structural study the structural parameters and spatial distri-
parameters (site occupancy, atomic coordinates, bution of Li ions in the Li-doped lanthanum
atomic displacement parameters, etc.) are determined
by a least square means so that the intensity data titanate. Moreover, neutron diffractiometry is
calculated using equation (5.2.19) and so on reproduce very effective in determining the position of
the measured intensity data. A noticeable difference hydrogen atoms. Because hydrogen raises the
in equation (5.2.19) between neutron and XRD is the background, it is preferable to carry out experi-
scattering power of jth atom. The X-ray is scattered ments by using the sample substituted for the
by electrons, thus the X-ray scattering power (atomic
scattering factor) increases monotonously with the deuterium as long as it is possible to do.
atomic number (Fig. 5.2.5). On the contrary, neutrons 2. Neutron can distinguish atoms with similar
are scattered by the nucleus and its scattering power atomic numbers from each other. For example,
(neutron scattering length) does not change monoto- the occupancy factors of oxygen and nitrogen
nously (Fig. 5.2.5). All the X-ray scattering powers atoms can be determined precisely, which is dif-
are plus, while some of neutron scattering powers
are minus (Fig. 5.2.5). The X-ray scattering power ficult in the case of XRD. Neutron diffractome-
decreases with Bragg angle, while the neutron try is effective for determining the positions of
scattering power is independent of Bragg angle. nitrogen and oxygen atoms in oxynitrides.
275