Page 409 - Book Hosokawa Nanoparticle Technology Handbook
P. 409
6.9 PROPERTIES OF GAS PERMEATION AND SEPARATION MEMBRANES FUNDAMENTALS
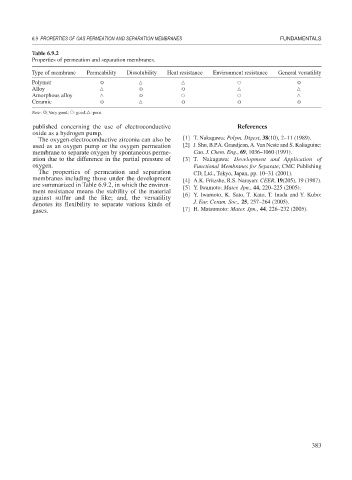
Table 6.9.2
Properties of permeation and separation membranes.
Type of membrane Permeability Dissolubility Heat resistance Environment resistance General versatility
Polymer
Alloy
Amorphous alloy
Ceramic
Note: ; Very good; : good; : poor.
published concerning the use of electroconductive References
oxide as a hydrogen pump.
The oxygen-electroconductive zirconia can also be [1] T. Nakagawa: Polym. Digest, 38(10), 2–11 (1989).
used as an oxygen pump or the oxygen permeation [2] J. Shu, B.P.A. Grandjean, A. Van Neste and S. Kaliaguine:
membrane to separate oxygen by spontaneous perme- Can. J. Chem. Eng., 69, 1036–1060 (1991).
ation due to the difference in the partial pressure of [3] T. Nakagawa: Development and Application of
oxygen. Functional Membranes for Separate, CMC Publishing
The properties of permeation and separation CD, Ltd., Tokyo, Japan, pp. 10–31 (2001).
membranes including those under the development [4] A.K. Fritzshe, R.S. Narayan: CEER, 19(205), 19 (1987).
are summarized in Table 6.9.2, in which the environ- [5] Y. Iwamoto: Mater. Jpn., 44, 220–225 (2005).
ment resistance means the stability of the material [6] Y. Iwamoto, K. Sato, T. Kato, T. Inada and Y. Kubo:
against sulfur and the like; and, the versatility
denotes its flexibility to separate various kinds of J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 25, 257–264 (2005).
gases. [7] H. Matsumoto: Mater. Jpn., 44, 226–232 (2005).
383