Page 484 - Book Hosokawa Nanoparticle Technology Handbook
P. 484
APPLICATIONS 8 DEVELOPMENT AND MULTI-FUNCTIONALIZATION OF HIGH-FUNCTIONAL SEPARATION MEMBRANES
(a) (b)
Glass Matrix Glass Matrix
a
x
tri
Glas
s M
Surface modification by
organosilicon compound
organosilicon compound
OH O
O
O Si
OH O O
OH OH OH OH Si O
Si SO H Si Si
-
- Si + 2
SO H
- 2
SO H + SO H SO H
-
-
+ 2 - 2
-
OH SO - H SO H + 2 SO 2 H
OH + 2 + 2 - +
OH SO 2 H
+
OH OH OH SO 2 - H Si SO 2 - H SO 2 - H Si
+
+
+
Si O Si Si O
O Si
O O O
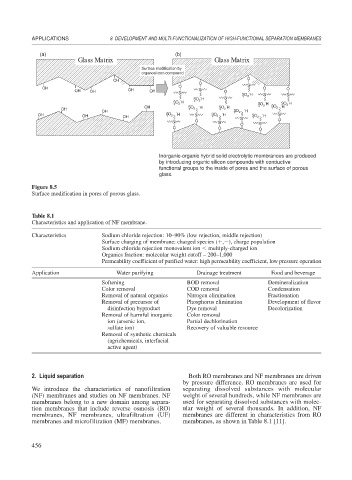
Inorganic-organic hybrid solid electrolytic membrances are produced
by introducing organic silicon compounds with conductive
functional groups to the inside of pores and the surface of porous
glass.
Figure 8.5
Surface modification in pores of porous glass.
Table 8.1
Characteristics and application of NF membrane.
Characteristics Sodium chloride rejection: 10–90% (low rejection, middle rejection)
Surface charging of membrane: charged species ( , ), charge population
Sodium chloride rejection monovalent ion multiply-charged ion
Organics fraction: molecular weight cutoff – 200–1,000
Permeability coefficient of purified water: high permeability coefficient, low pressure operation
Application Water purifying Drainage treatment Food and beverage
Softening BOD removal Demineralization
Color removal COD removal Condensation
Removal of natural organics Nitrogen elimination Fractionation
Removal of precursor of Phosphorus elimination Development of flavor
disinfection byproduct Dye removal Decolorization
Removal of harmful inorganic Color removal
ion (arsenic ion, Partial dechlorination
sulfate ion) Recovery of valuable resource
Removal of synthetic chemicals
(agrichemicals, interfacial
active agent)
2. Liquid separation Both RO membranes and NF membranes are driven
by pressure difference. RO membranes are used for
We introduce the characteristics of nanofiltration separating dissolved substances with molecular
(NF) membranes and studies on NF membranes. NF weight of several hundreds, while NF membranes are
membranes belong to a new domain among separa- used for separating dissolved substances with molec-
tion membranes that include reverse osmosis (RO) ular weight of several thousands. In addition, NF
membranes, NF membranes, ultrafiltration (UF) membranes are different in characteristics from RO
membranes and microfiltration (MF) membranes. membranes, as shown in Table 8.1 [11].
456